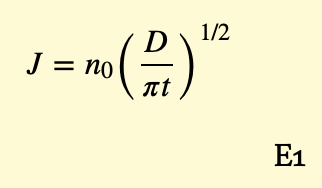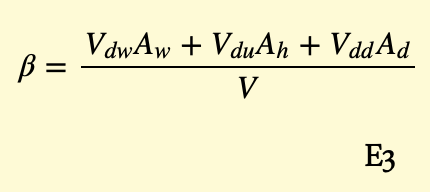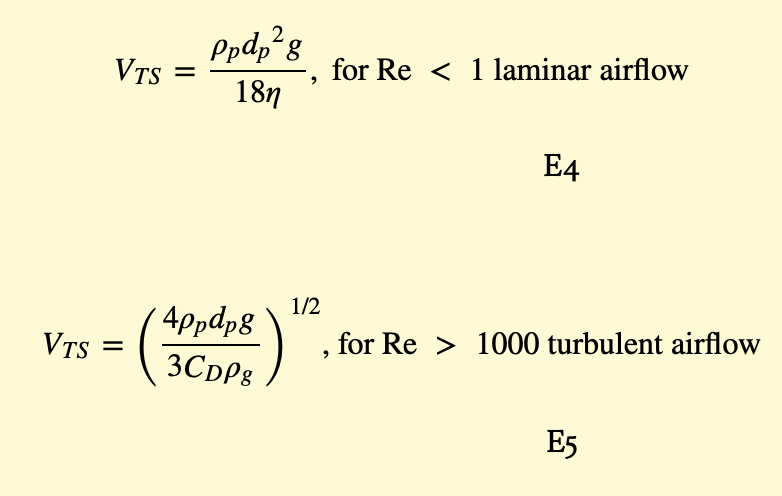Thermal Inversion and Pollution
There is a strong correlation
between thermal inversion and air pollution in
Fairbanks, Alaska and other locations around the
world with similar environmental conditions.
If you are interested in learning about how thermal inversion is related to air pollution through my research, continue reading »