
http://inspiringgoodliving.com/bbq-battle-charcoal-vs-gas-grill-2/
Step 1: Fuel Source
Coal is formed
by natural earth processes just like petroleum and
natural gas. As plants and animals die, their organic
matter builds up and is covered with layers of
sediment. Over time, the temperature and pressures the
organic matter is exposed to will transform it into
coal. 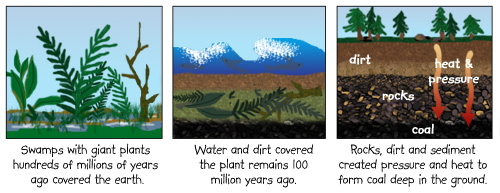 https://hec-r.s3.amazonaws.com/Site/prod/contentplayer/templates/kids/images/coal01.jpg The composition of the organic matter determines whether it will form coal, petroleum or natural gas. Wood tends to form coal based on its high levels of carbon and relatively low levels of oxygen that get trapped underground with the wood. However, any organic matter can form any hydrocarbon based on a myriad of factors, including the environment and surrounding material. Coal formed underground varies in its quality, which is based on the carbon content. The higher the carbon content, the more valuable the coal. HOWEVER..... In our grill we will not be using natural coal, as it is better suited to industrial purposes. Charcoal used for grills is a specific type of man-made coal that is produce by heating wood in a low oxygen environment. The result is charred wood, which is what we call charcoal. This combustion reaction for wood is shown below. 6 C10 H15 O7 (s) + heat → C50 H10 O (s) +10 C H2 O (g)
|
Step 2: Converting Charcoal to Heat
| Charcoal grills
are more simple to use as their are no gas lines or
tanks involved, and we need only to ignite our coal.
Once our coal is lit it will continue to burn.
However, many things burn when we light them so what
is it about coal that makes it so special and valuable
as a heat producing source? Coal is made up of carbon and hydrocarbons, which produce relatively large amounts of heat when they undergo combustion. Since we know the molecular formula for char, we know that it is mostly carbon. The combustion reaction of carbon is exothermic, which means it releases energy. In our case, this energy is released in the form of heat. The combustion reaction of carbon is shown below. C + O2 → CO2 + heat The coals maintain their burn for two reasons. First of all, they are a dense source of carbon fuel. Secondly, the combustion reaction of char is relatively slow due to the large amount of carbon in one molecule. The result is a steady, long-lasting supply of heat for a seemingly small amount of fuel. |
Title Page Method 1: Gas Grill Method 2: Charcoal Grill Understanding The Cooking Process Bibliography

