History
In 1878 Rudolf
Diesel first came up with the idea of a diesel engine. By 1892
he had manufactured the first diesel engine (Brain, 2000).
Diesel engines
have evolved greatly, from power to emissions. Diesel engines
have a bad record of high carbon output and other releases
into the atmosphere. The government now put regulations on the
allowable emissions to protect the environment. Engine
manufacturers are now trying to make the most powerful engines
while being environmentally friendly. Diesel is being burned
more efficiently so that the energy can be transformed without
losing it to the system, therefore more energy can be
transferred to the flywheel. This makes for better fuel
economy and increased power. Power in engines is usually given
in Horsepower.
Power = Work / Time = Watt
1 Horsepower = 746 Watts
(Knight, 2004)
As technology
has grown, so has the control over diesel engines. Computers
now keep tight control on how an engine runs based on
temperature, pressures, and sensors that give feedback to
different parts of the engine.
Sensors are
used to test the exhaust to make sure that it is complying
with governmental regulations (Technology, 2013). This
information is read by the computer and accounted for while
telling the engine how to run.
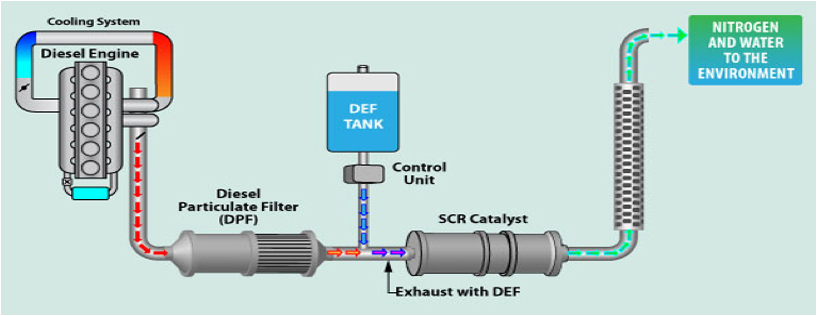
The second
image gives the process of diesel exhaustÕs flow and how it is
regulated to be safer for the environment.

2. http://ppcdefsolutions.com/images/def.jpg