Background
Information Background
Information
The vision process is primarily due to light, refraction, lenses and the
interactions among them.
Light
Without light there is no vision. The nature of
light can be difficult to describe, since it can
behave as a particle, behave as a wave, or show a
combination of the two. Because of this, three
models of light have been made to describe the
behavior of light for different situations. The
wave model, the ray model, and the photon model.
Since we are discussing the process of vision, the
ray model of light is the most appropriate
to use. Some basic ideas of this model are:
- Light travels in
straight lines in the form of rays
- These light rays
can cross each other
- Unless light
interacts with matter, it will travel
forever
- An object is a
source of light rays, objects can be:
- self
luminous, such as the sun,
- reflective,
where light is reflected in all
directions.
Refraction
Two things happen when
light reaches a boundary between two transparent
mediums, reflection and refraction. Refraction
is when light rays bend and change direction as
they travel across the boundary into the second
medium.
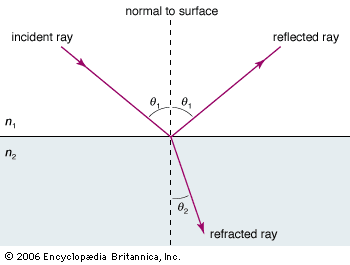 In the image to the right the
angle of incidence and the angle of refraction
are related by Snell's law of refraction: In the image to the right the
angle of incidence and the angle of refraction
are related by Snell's law of refraction:
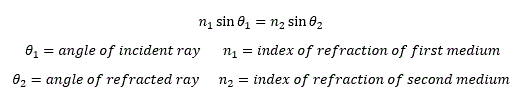
The index of refraction (n) for a
transparent medium is defined as:
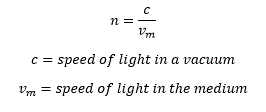
http://pmr-science.wikispaces.com/Students%27+Contribution+-+1.7+Light+and+Sight
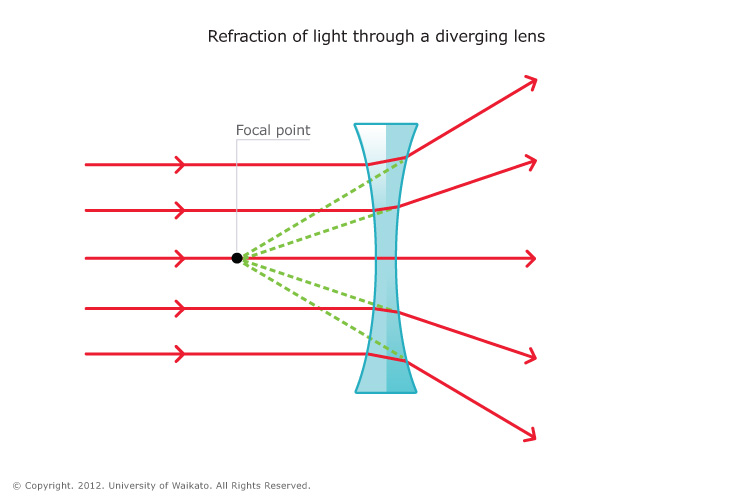
Lenses
Vision works by by focusing
diverging rays from an object onto the retina of the
eye, and from the point where the rays diverge is
where the object appears to be. This ability to
focus diverging rays of light is due to a lens,
which uses refraction at curved surfaces. Two types
of lenses are converging (also known as convex) lens
and diverging (also known as concave) lens.
A converging lens causes rays to bend toward
the optical axis, while a diverging lens
cause rays to bend away. However as light passes
through the center of these lens; the rays do not
bend while continuing in the same direction. The focal
point of the lens is where the
light rays converge. and the distance from the focal
point to the lens is called the focal length.
|
 Background
Information
Background
Information In the image to the right the
angle of incidence and the angle of refraction
are related by Snell's law of refraction:
In the image to the right the
angle of incidence and the angle of refraction
are related by Snell's law of refraction: