| Home |
Heat Transfer |
How it Works |
What it is Used For |
Facts |
Bibliography |
http://swh.schoolworkhelper.netdna-cdn.com/wp-content/uploads/2010/08/Convection-Conduction.jpg?c71720
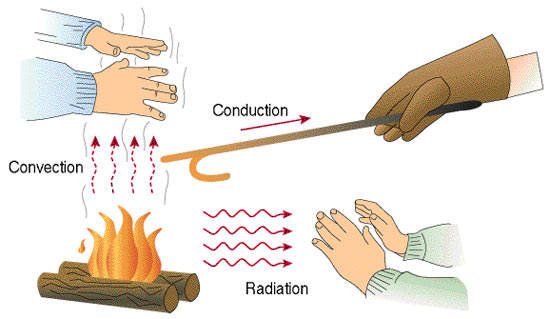
Heat transferring is the process in which thermal energy is exchanged between two or more separate systems. The transfer of thermal energy usually occurs from a high temperature object to a lower one. There are three types of Heat transfer: Conduction, Convection and Radiation.
Conduction is the exchange of energy without motion. For example, if one end of a metal cylinder is placed in a fire, heat will move toward the colder end because the particle velocities in the hotter region are moving faster than the particles in the colder region and cause collisions which create energy.
Heat Conduction can be calculated by the equation:
Where k is the thermal conductivity of the barrier and d is the thickness.

http://www.hk-phy.org/contextual/heat/hea/condu/conduction_e.gif
Convection is energy transfer by the motion of mass such as a fluid. When a fluid is heated the gases will start to expand near the heat source and become less dense. When the gas expands enough it rises to the colder area and cools down again. The process continues until the system reaches an equilibrium temperature. If heat is constantly being added to the system, circular currents are created where the hot fluid rises where it cools off and returns to it's original density and falls back down creating convection currents.
http://www.physics.arizona.edu/~thews/reu/Convection.bmp
Radiation is energy lost by electromagnetic waves that radiate from an object. This is one way people often lose heat. Thermal Radiation can be calculated by the Stefan-Boltzman law which is as follows:
P=eσA(T^4-T_C^4)

http://www.drcruzan.com/Images/Physics/Thermodynamics/HeatTransfer/HeatTransferModes.png