Real World Uses of Arduinos
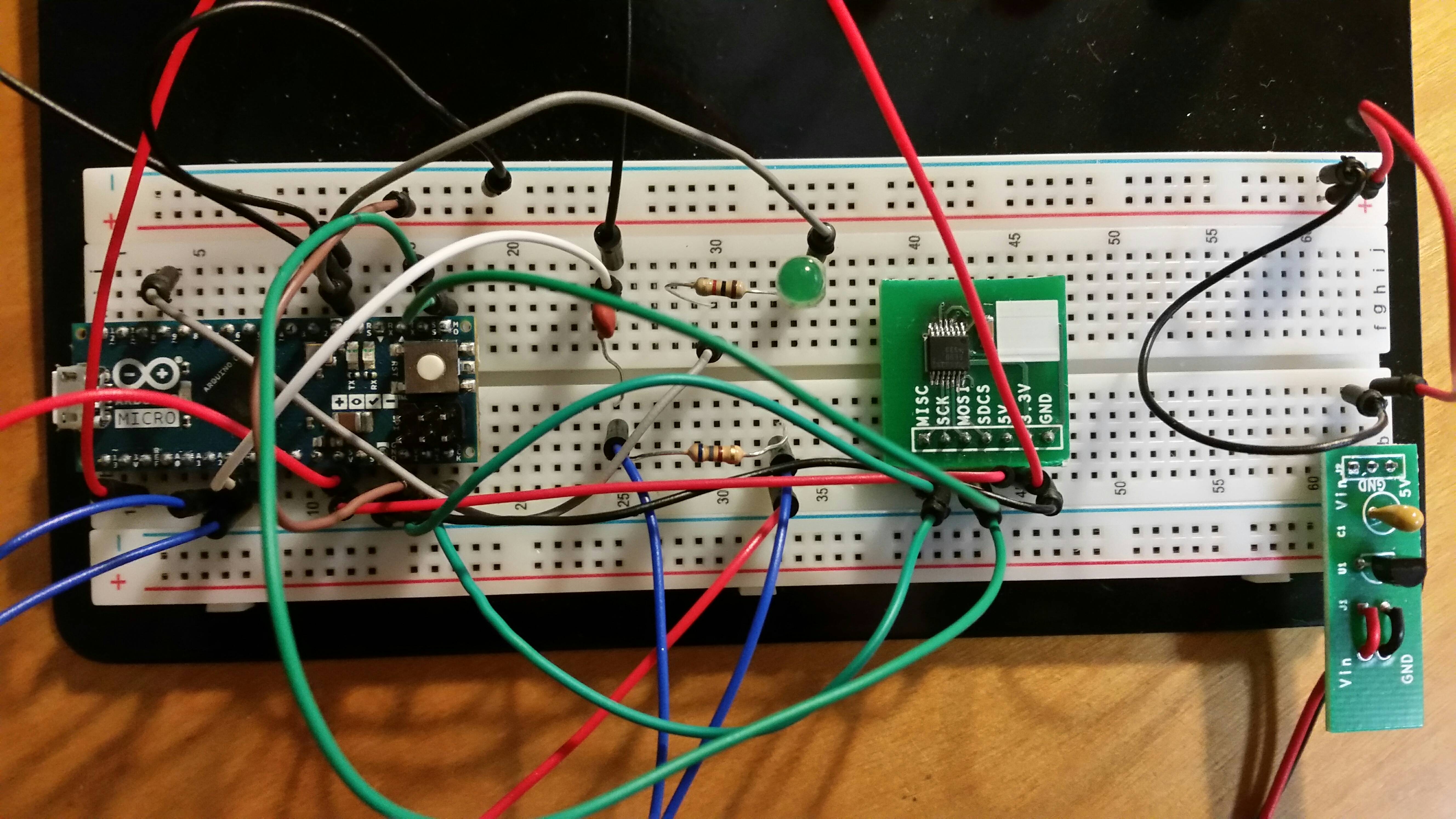
 For an Electrical Engineering project earlier this semester, I used the Arduino platform to create the temperature logger shown above that utilized the Steinhart-Hart equation to accurately record temperature by observing the varying resistance in a component known as a thermistor. This data was then stored to an SD card in a format that could later be easily opened in Microsoft Excel. Without the easily adaptable Arduino platform, this project would not have been nearly as simple as it was and would have required more components and extensive electrical analysis using Kirchoff's Current Law, Kirchoff's Voltage Law and known fundamentals about transistors, diodes, and various other components that work behind the scenes on the pictured Arduino Micro board.
For an Electrical Engineering project earlier this semester, I used the Arduino platform to create the temperature logger shown above that utilized the Steinhart-Hart equation to accurately record temperature by observing the varying resistance in a component known as a thermistor. This data was then stored to an SD card in a format that could later be easily opened in Microsoft Excel. Without the easily adaptable Arduino platform, this project would not have been nearly as simple as it was and would have required more components and extensive electrical analysis using Kirchoff's Current Law, Kirchoff's Voltage Law and known fundamentals about transistors, diodes, and various other components that work behind the scenes on the pictured Arduino Micro board.

https://hackster.imgix.net/uploads/cover_image/file/48893/IMG_8744.Immagine003.jpg?auto=compress%2Cformat&w=400&h=300&fit=min

https://blogs.scientificamerican.com/budding-scientist/files/2012/09/Screen-shot-2012-09-27-at-10.55.36-PM.png

http://makezine.com/wp-content/uploads/2014/03/bluetoothlock_entercode.jpg
Throughout the world there are various innovative and inspiring arduino-based projects such as the ones shown above. The platform can be used for a wide arrange of things from drones to internet connected (also known as Internet of Things) doorlocks. The possibilities of what can be created using this versatile tool are endless and the future of Arduino now exists more in the eye of an artist rather than that of an engineer, which was always its endgoal. So as the world becomes evermore connected, the knowledge gap that separates the dreamers and doers of the world will become less prominent and this will be largely due to the groundwork set by Arduino.