Engines |
Engines
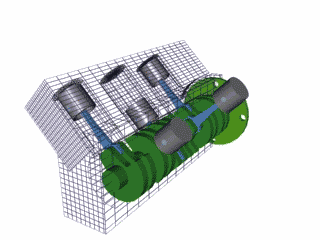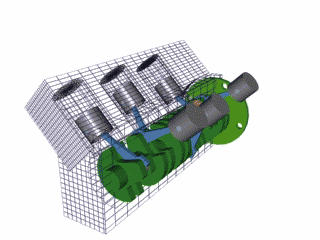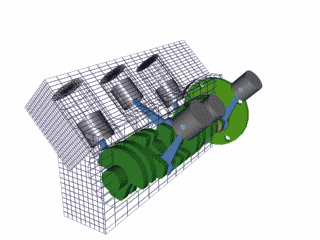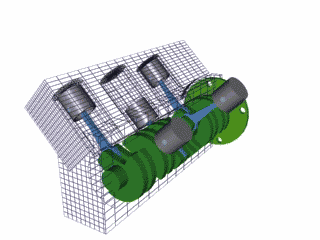
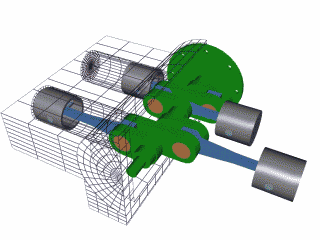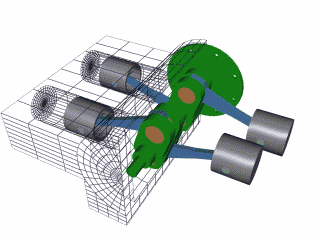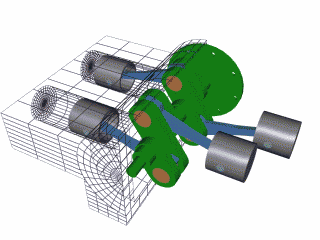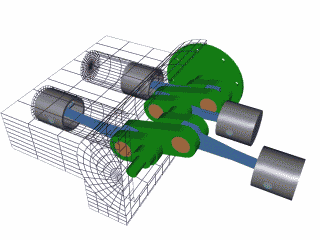
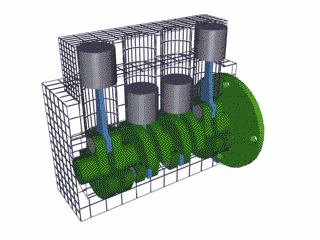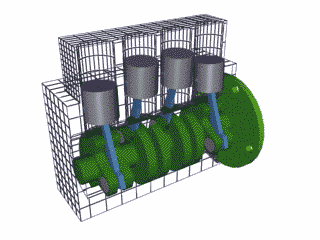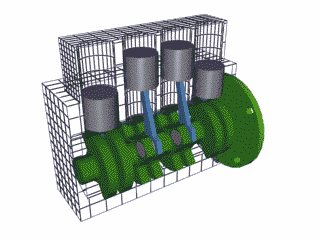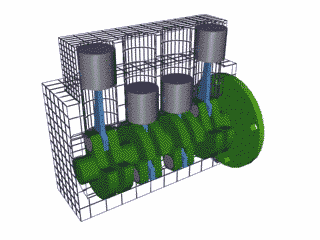
The 4 stroke cycle happens thousands of times a minute and the tachometer reads how many revolutions the crankshaft makes per minute or 'rpm,' with some engines reaching as high as 10,000 rpms! Electronics control how much fuel to add and the precise timing to ignite the spark plugs, while the timing belt synchronizes the camshaft with other moving parts inside the motor so everything runs smoothly (Brain & Hall-Guisler, 2018). There are all kinds of ways to increase engine performance, such as adding more cylinders, increasing the cylinder volume, changing the piston orientations, increasing the oxygen density, and many, many more! Some engines arrange the cylinders in a V shape like a V8 Corvette or V6 Mustang, while others lie flat, referred to as a "boxer" engine because of the way the pistons move, such as a Porsche 911. Inline engines have the cylinders lined up 'in a line' and only a handful of cars use a rotary engine. The rotary, also known as wankel, was a unique design that had a triangular disc spin around the crankshaft and all the strokes would be happening simultaneously in a oblong chamber. The rotary engine was supposed to smaller and more efficient that regular piston design with less moving parts, but when things went wrong, the entire engine had to be taken apart, often with many parts and seals needing to be replaced.