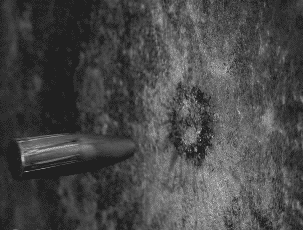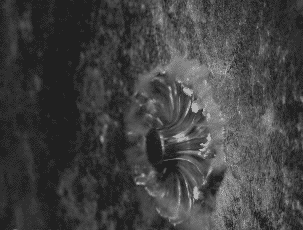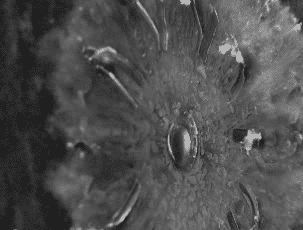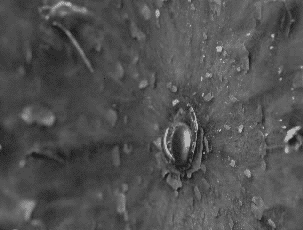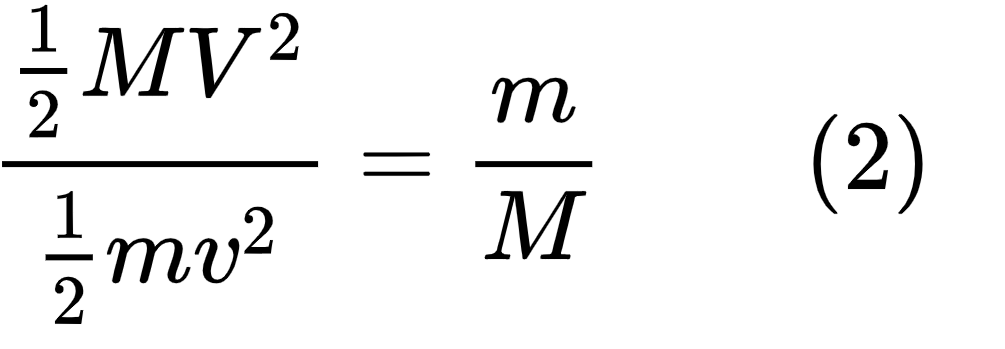|
The bullet whistles through the air, fighting it are the forces of momentum and gravity, push and pull. Finally hitting its mark, the bullet imparts kinetic energy to the target equivalent to half of its mass multiplied by its velocity squared.
|
Kinetic Energy
|
Kinetic energy is experienced by both the shooter and the target, to the shooter when the bullet is fired and to the target when the bullet makes impact. However, though both experience kinetic energy, the KE imparted to the shooter is far less than that given to the bullet due to the shooters greater mass. M = mass of shooter, V = velocity of shooter, m = mass of bullet, v = velocity of bullet.
|
Ratio of KE shooter to KE of bullet
|
Ballistic Gel Test from americanhandgunner.com demonstrates the displacement of a bullets penetration after impact.
|
Work Done
Work done by the bullet on the target is equivalent to the change in kinetic energy, this change is equal to the kinetic energy since the bullet was at rest before firing.
Net Force
The net force of the bullet on the target is equal to the work done divided by the displacement. Displacement refers to how far the bullet travels after hitting the target, meaning how far does the bullet penetrate. The greater the displacement of the bullet, the less force that is passed on to the target. This formula is used to describe Stopping Power, a term focused around the idea that slower and generally larger less penetrative rounds impart more force on a target to a certain degree than smaller fast moving penetrative rounds since they stop within a shorter distance.
Create a free web site with Weebly