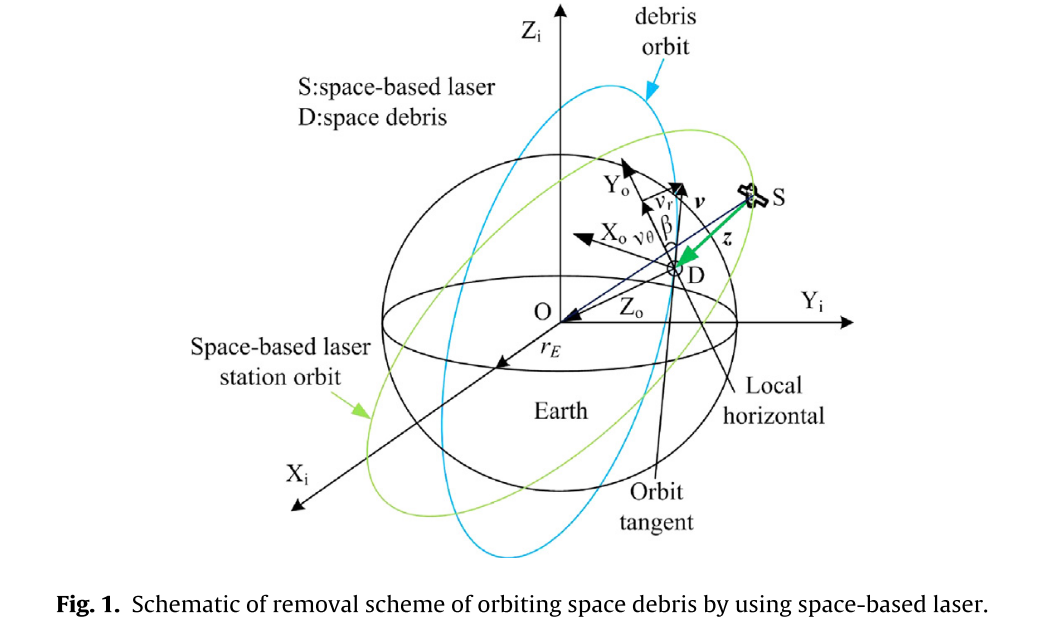
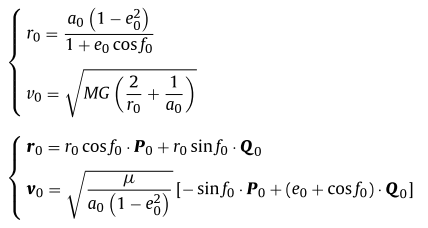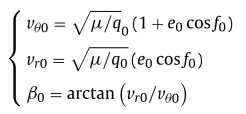Space Debris Removal Systems
Space debris low in Earth's
orbit has become a significant threat to current
and future spacecraft missions.
- Space debris can collide
with and damage spacecraft.
- These collisions contribute to the cascade effect of space debris.
- As a result, space debris
has become smaller and harder to detect by
current systems.
If you are interested in learning about possible methods for active debris removal and technological methods of detecting and avoiding debris, continue reading »