 locity
& Acceleration in Volleyball
locity
& Acceleration in VolleyballAcceleration occurs when
there is an increase in velocity. This can be achieved
in volleyball by a few tricks.
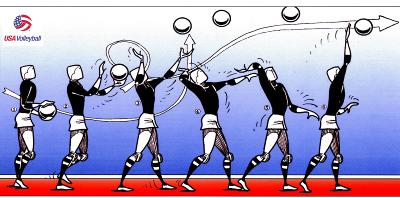
Acceleration that occurs without the aid of the player happens because of the downward force of gravity. A player can also create top spin on the ball to make the ball accelerate towards the ground. A player achieves this by snapping their wrist at the optimum time. If a player does not snap their wrist, the serve floats and does not drop to the floor as fast.
Acceleration that occurs without the aid of the player happens because of the downward force of gravity. A player can also create top spin on the ball to make the ball accelerate towards the ground. A player achieves this by snapping their wrist at the optimum time. If a player does not snap their wrist, the serve floats and does not drop to the floor as fast.
When using the equation to
find the velocity of an average serve directly after it
crosses the net, we would get a velocity of 5.29 meters per
second.
Velocity = (9 meters) / (1.7 seconds) = 5.29 m/s
Velocity = (9 meters) / (1.7 seconds) = 5.29 m/s
Acceleration
V = (Distance traveled) /
(Time passed)
From the serving line to the net on an inside court, the distance is nine meters. An average serve ranges from 20 to 40 mph, which would be around 1.7 seconds to .85 seconds.
From the serving line to the net on an inside court, the distance is nine meters. An average serve ranges from 20 to 40 mph, which would be around 1.7 seconds to .85 seconds.
The velocity can be
calculated for any play in volleyball, including the serve,
set, attack, and pass. The equation below demonstrates the
velocity of an average float serve
Velocity
Velocity is the speed of
movement. In volleyball, there is quite a bit of movement.
There is movement from the players, and especially the ball.