Dr. Dan P. Clemens' Article
Dr. Dan P. Clemens
Boston University
Clemens, 1985[5]
Clemens used radial velocity data of carbon monoxide, CO, clouds in the Milky Way which are interior to our orbit. The radial velocity is obtained using the Doppler method. Since the clouds are large, parts of the clouds are going to appear to be moving faster. Thus, when you look at cloud, you are going to get a velocity distribution. We can see this by looking again at out velocity sketch for stars

If the star was at a position such that r was perpendicular to R, the radial velocity would be largest as all of rotational velocity would be in the radial direction.
By analysing the radial velocity distribution of the clouds, and picking the largest velocity, Clemens could find the rotational velocity of the clouds. This method is call tangent point detection.
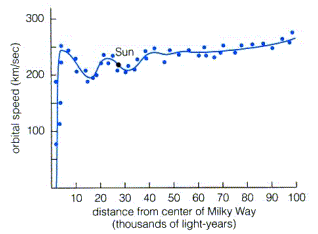
Clemens then used radial velocity data of CO and HII clouds at radii larger than our orbital radius. Combining all this data together, Clemens was able to fit a curve to the data giving us the rotation curve shown below.
[6]
That concludes my dark matter website. The references I used to compile this website can be found here:
If you would like to know more about this website, and the designer, go here: