What do cardiologists do?
http://www.againfaster.com/articles/a-second-opinion.html
Face to face
Cardiologists sit down with their patients and discuss what is going on, explain what tests they may need to perform, and answer questions the patient/family may have. There are some diagnostic tests/procedures that the cardiologist might be present for; however there are also many that they do not need to be present for and are handled by technicians or nurses.
Gotta stay smart!
Cardiologists continue to learn about their field throughout their career by completing continuing education credits (CEUs), research, reading medical journals, even the cases they work on from day to day can be a learning experience. It is very important for them to stay up to date on the medical field in general, but especially on their specialty. I mean seriously, would you want to go to a doctor who had learned anything new since 1978?
Procedures/Diagnostic Tests
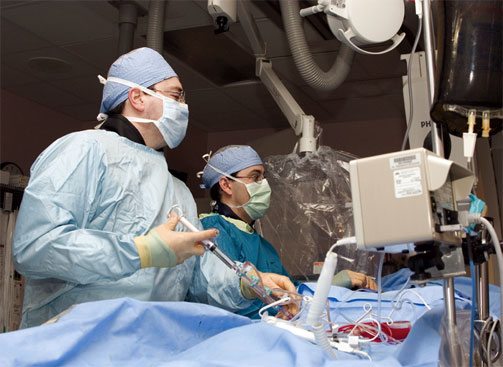
Cardiologists participate in procedures as simple as a stress test (can also be done by other doctors, and in some hospitals by nurses or technicians) and as complicated as surgery. When they don't participate in a diagnostic test, like an EKG, they go over it. EKGs are typically done in a hospital by a CNA or a cardiology technician, but a doctor looks over every single one (each doctor reviews different ones, there isn't just one doctor whose sole responsibility is looking at and assessing EKGs). Examples of procedures that may be performed are angiograms, open heart surgery, angioplasty, stent placement, and pacemaker placement. There are also many other procedures that cardiologists may perform.
Some diagnostic tests that may be done concerning the heart:
Electrocardiogram (EKG) - 10 stickers (or 13 for infants and smaller children) on your body hooked up to a machine by leads that looks at the electrical activity of your heart. There is one sticker for each of your limbs; arm leads are typically placed on your shoulders, and legs leads are on your ankles or waist depending on the person who performs it. One that goes on the right side of your sternum, and 5 that go on the left curved down around your heart. Proper placement of the stickers and the leads that attach to them is important to being able to read the EKG.
Echocardiogram - An ultrasound of your heart that allows the doctor, echo technician, and anyone else present to view your heart in real time. They watch as it beats, and the tech takes several pictures in different views for the doctor to review.
Exercise Stress Test - You are hooked up to a continuous EKG that the doctor monitors as you walk on a treadmill and the person performing the test (usually the doctor) sets it to the proper protocol so the speed and incline increase until you reach a target heart rate.
Chemical Stress Test - A chemical is injected into your vein that simulates stress on your heart by dilating the arteries in a similar fashion as it would during exercise. These tests do not give as much information as an exercise stress test and are typically done with a nuclear tracer also being injected so they can take images of your heart to observe blood flow after you are monitored a few minutes and unhooked from the EKG.


