Maxwell's
equations describe how electricity and magnetism relate to their
sources and how they work.
Gauss's Law: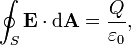 This
Law
states,
put simply, that the electric flux through any closed
surface is proportional to the enclosed electric charge.
This
Law
states,
put simply, that the electric flux through any closed
surface is proportional to the enclosed electric charge.
wikipedia.org
Gauss's Law for Magnetism: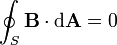 This
law
states
that for each "volume space" there are just as many magnetic
field lines going in as there are going out.
This
law
states
that for each "volume space" there are just as many magnetic
field lines going in as there are going out.
wikipedia.org
Faraday's Law of Induction: This
law
states
that the induced electromotive force in any closed circuit
is equal to the time rate of change of the magnetic flux through the
circuit.
wikipedia.org
This
law
states
that the induced electromotive force in any closed circuit
is equal to the time rate of change of the magnetic flux through the
circuit.
wikipedia.org
Ampere's Law with Maxwell's correction: This
law relates the magnetic field around a closed loop to the electic
current passing in the loop.
wikipedia.org
This
law relates the magnetic field around a closed loop to the electic
current passing in the loop.
wikipedia.org
Gauss's Law:
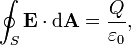 This
Law
states,
put simply, that the electric flux through any closed
surface is proportional to the enclosed electric charge.
This
Law
states,
put simply, that the electric flux through any closed
surface is proportional to the enclosed electric charge.wikipedia.org
Gauss's Law for Magnetism:
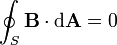 This
law
states
that for each "volume space" there are just as many magnetic
field lines going in as there are going out.
This
law
states
that for each "volume space" there are just as many magnetic
field lines going in as there are going out.wikipedia.org
Faraday's Law of Induction:
 This
law
states
that the induced electromotive force in any closed circuit
is equal to the time rate of change of the magnetic flux through the
circuit.
wikipedia.org
This
law
states
that the induced electromotive force in any closed circuit
is equal to the time rate of change of the magnetic flux through the
circuit.
wikipedia.orgAmpere's Law with Maxwell's correction:
 This
law relates the magnetic field around a closed loop to the electic
current passing in the loop.
wikipedia.org
This
law relates the magnetic field around a closed loop to the electic
current passing in the loop.
wikipedia.org