



In 1676
Newton amended mathematics by proving
that the sum of a series with negative n
integers converges, or reaches a certain value when summed to infinity when the absolute value of x
is less than 1.
Newton
also polished the work of his professor Isaac Barrow who was the first
Lucasian
Professor of Mathematics and Natural Philosophy at Cambridge and came
up with
what is known as the Fundamental Theorem of Calculus:
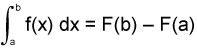
http://archives.math.utk.edu/visual.calculus/4/ftc.9/
By adding an
infinite amount of
diminutive rectangles under any continuous curve with an initial point
on the
curve a to the final point b being
integrated, the difference
between two functions F(b)-F(a) is
obtained.
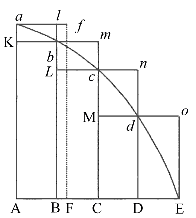
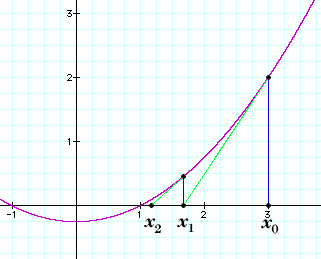
It is important to mention that without the use of the integral and the derivative, it would be much more difficult for physicists and engineers to improve living conditions of society or even come up with luxuries such as televisions, electricity, cars, etc; since calculus is the base for determining the proper function of such creations.