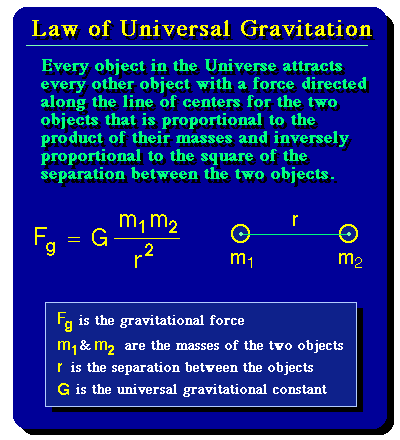
But why doesn’t the moon collapse with the earth as the apple did?
Newton reasoned that the moon travels at a constant acceleration around the earth and is projected at the right velocity, thus creating its own orbit since the constant velocity and attraction by both bodies set a path for the moon to follow.
http://csep10.phys.utk.edu/astr161/lect/history/newtongrav.html
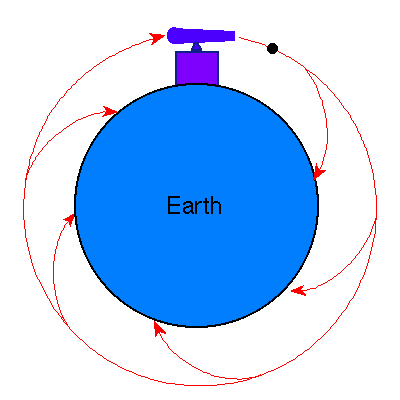
Here, the same concept applies, if the velocity of the cannon ball is adjusted to the right speed, there will be a point where the cannon ball will create a uniform path and create its own orbit!!!!!!!