
LAWS OF MOTION
Newton not only came up with the Law of Universal Gravitation, he also developed the three laws of motion. The four laws were all introduced and explained in Principia Mathematica, a book he wrote in 1687, which is considered one of the greatest scientific books ever writen.

http://www.historyguide.org/images/principia.jpg
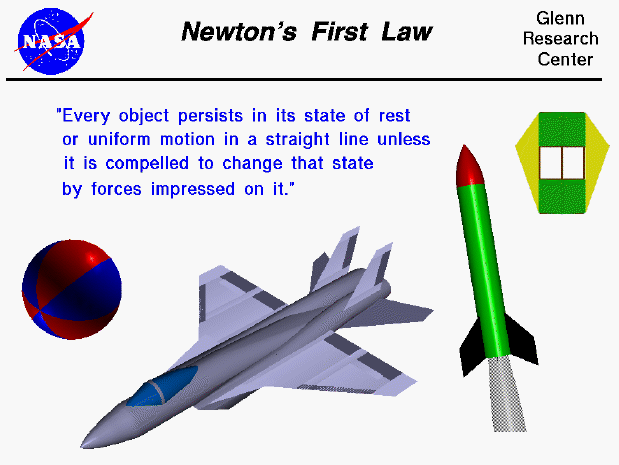
Newton ’s First Law of Motion: A body at rest remains at rest or a body in motion remains in motion unless acted on by an external force.
www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/ K-12/airplane/newton3.html
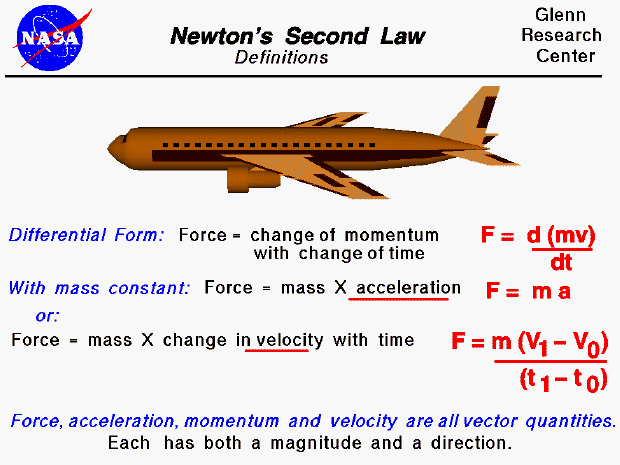
Newton ’s Second Law of Motion: When viewed from an inertial reference frame, the acceleration of an object is directly proportional to the net force action on it and inversely proportional to its mass. In mathematical terms: ∑ F=ma where ∑ F is the net force acting on an object, ‘m’ is the mass of an object, and ‘a’ is the acceleration of an object.
www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/ K-12/airplane/newton3.html
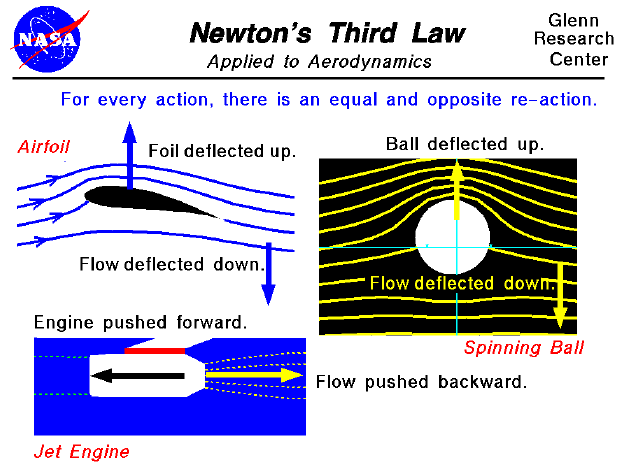
Newton ’s Third Law of Motion: For every action force there is an equal and opposite reaction force.
www.grc.nasa.gov/WWW/ K-12/airplane/newton3.html