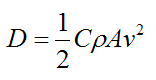Picture retrieved from http://ffden-2.phys.uaf.edu/212_spring2007.web.dir/jessica_gonowon/gonowon_page2.html
Drag force is the reason why in the real world, if we drop a feather and a rock from the same height, they would never reach the ground at the same time even though the gravitational force acting on them is exactly the same. Drag force, as known as air resistance, is caused by all the gas molecules in the air. Sure, we can't see it, but that doesn't mean that they don't exist. Think of it like water, we have to push away the water molecules when swimming. The same concept applies to air resistance, except we barely feel any of that resistance in our daily life. However, when we move at a great speed, we start to feel more and more resistance.
Drag force is defined as a resistance force on an object as it moves through a fluid such as water or air. The direction of drag force is always opposite to the direction of the velocity of the object.
Picture retrieved from http://www.real-world-physics-problems.com/drag-force.html
D is drag force
C is the drag coefficient
p (rho) is the density of the fluid
A is the cross-sectional area of the object
v is the speed of the object relative to the fluid
C is the drag coefficient
p (rho) is the density of the fluid
A is the cross-sectional area of the object
v is the speed of the object relative to the fluid
As you can see, the drag force is dependent on all these factors. Since the cross-sectional area of the object affects the force, skydivers can change their speed by adjusting their body position when falling.