When ANFO or TNT ignites, there is
a rapid expansion in volume due to the chemical
reaction producing an enormous amount of
gas. When this takes place, the increase in
volume is essentially force being equally applied
to the surroundings in all directions.
In rock blasting, an explosion in the ground will
exert an equal amount of force in all
directions. It will exert an equal amount of
force on the material above as it will on the
matter below. However, the force exerted
below is canceled out by the normal force.
Essentially what this means is that an explosion
at the Earth's surface will not move the Earth by
any measurable amount. The matter above the
the explosion will move, because the force exerted
on it by the explosion is much greater than the
stress of the material; or force of the particles
holding each other together.
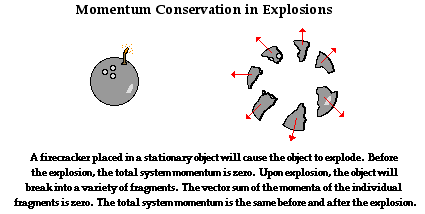 © physicsclassroom.com
© physicsclassroom.com
In an explosion, an internal impulse propels the
parts of the system in many direcitons.
After the explosion, the fragments of any material
impacted are sent in many directions and they all
have momentum. We can apply the concept of
momentum conservation to find that the vector sum
of all individual parts is equal to the momentum
of the initial impulse. [6]
