Even though only a small
percentage of the gases in Earth’s atmosphere are greenhouse
gases, they have a huge effect on Earth's climate. Since the
preindustrial era, humans have been increasingly emitting vast
amounts of greenhouse gases, offsetting the natural greenhouse
effect. The continuing increase in greenhouse gases in the
atmosphere trap more and more energy (heat) from leaving Earth
to space, further offsetting Earth's energy balance, thus
increasing Earth's global temperature.
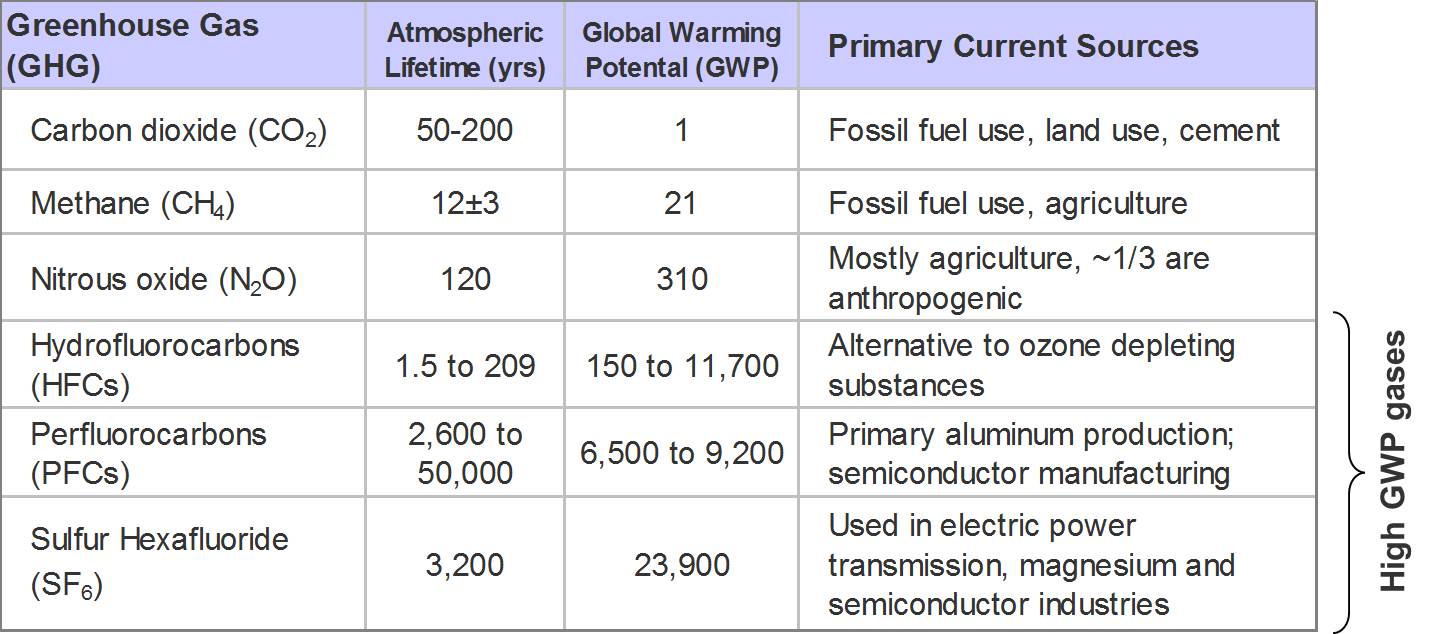
Figure from: http://priceoncarbon.org/wp-content/uploads/2015/01/All-GHG-Arent-Alike.jpg.
The table above the global warming potential
and atmospheric lifetime of the greenhouse gases. Global
warming potential is a measure of the estimated
contribution to global warming a gas has when it is
directly emitted into the atmosphere. This is because
certain gases, due to their chemistry, are more effective
at absorbing and remitting radiation in Earth's
atmosphere. The relative scale for global warming
potential works by comparing the same amount of mass of a
gas to that of carbon dioxide, which by convention has a
GWP of 1. The atmospheric lifetime of a gas is important
because it shows how long the gas will stay in the
atmosphere. For an example of how to read the chart,
methane's GWP is 21, which means that methane will cause
21 times as much warming as the same amount of mass of
carbon dioxide over a 100 year time period.
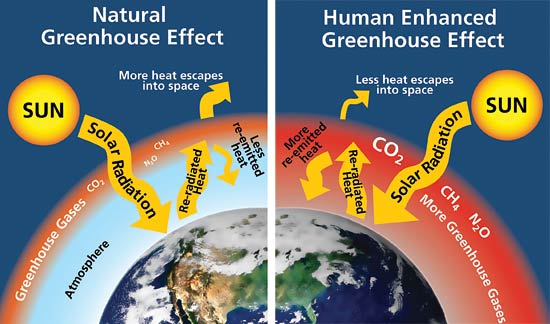
Figure from: https://mrgeogwagg.files.wordpress.com/2015/06/natural-and-enhanced-greenhouse-effect.jpg