Figure from: https://www.azosensors.com/images/Article_Images/ImageForArticle_8%281%29.gif
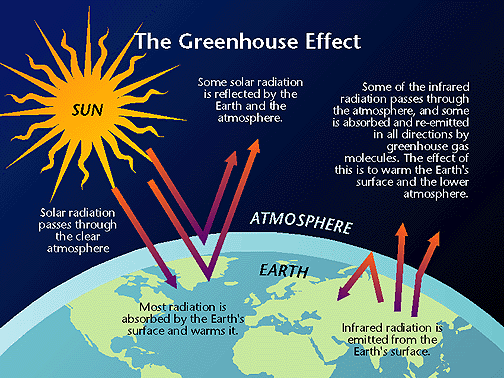
The greenhouse effect is the process where infrared radiation is absorbed by gases in the atmosphere, thus heating the Earth to a temperature above what it would be without any atmosphere. Our planet is livable due to green gases, because without the warming effect of these gases in the atmosphere, Earth's global mean temperature would be around -18 Celsius instead of the 15 Celsius it is today.
To understand the greenhouse effect it is important to understand the basics of blackbody radiation and what types of radiation the sun and Earth emit. Black bodies are bodies that absorb all the radiation that they receive and that emit radiation in all wavelengths. The wavelengths of radiation emitted by a body correspond to distinct energy ranges. The intensity of the radiation emitted by a blackbody depends on its temperature (intensity is proportional to T^4 ).
The Sun and Earth can both be simplified as black bodies. The radiation emitted from the Sun is mainly in short or visible wavelengths which corresponds to the Sun’s hot temperature (~ 5777 K), while the radiation emitted by the Earth to space is mainly in the infrared wavelength range, which corresponds to Earth's colder temperature (~ 298 K). As Earth’s temperature is mostly in a state of thermodynamic equilibrium, the incoming shortwave radiation should be balanced by the out-going long-wave radiation. However, because of the greenhouse gases, not all the long-wave radiation emitted by Earth leaves to space. This is because the greenhouse gases in the atmosphere can absorb Earth’s long-wave radiation and thus heat up the surrounding air by colliding with the other molecules. The heated (ie. excited) molecules can then radiate energy back to Earth’s surface. This process has the effect of trapping the outgoing long-wave radiation thereby heating up Earth’s atmosphere and surface, and is the reason why we use the term greenhouse effect to describe this process.
**Note the term
green-house effect is just used to describe increase in heat but
that atmospheric green-house effect is different from an actual
greenhouse because greenhouse gases block conductive heat loss,
while the glass in an actual greenhouse blocks convective heat
loss.