How Do They Impact Gravity Waves?

(5)
(6)
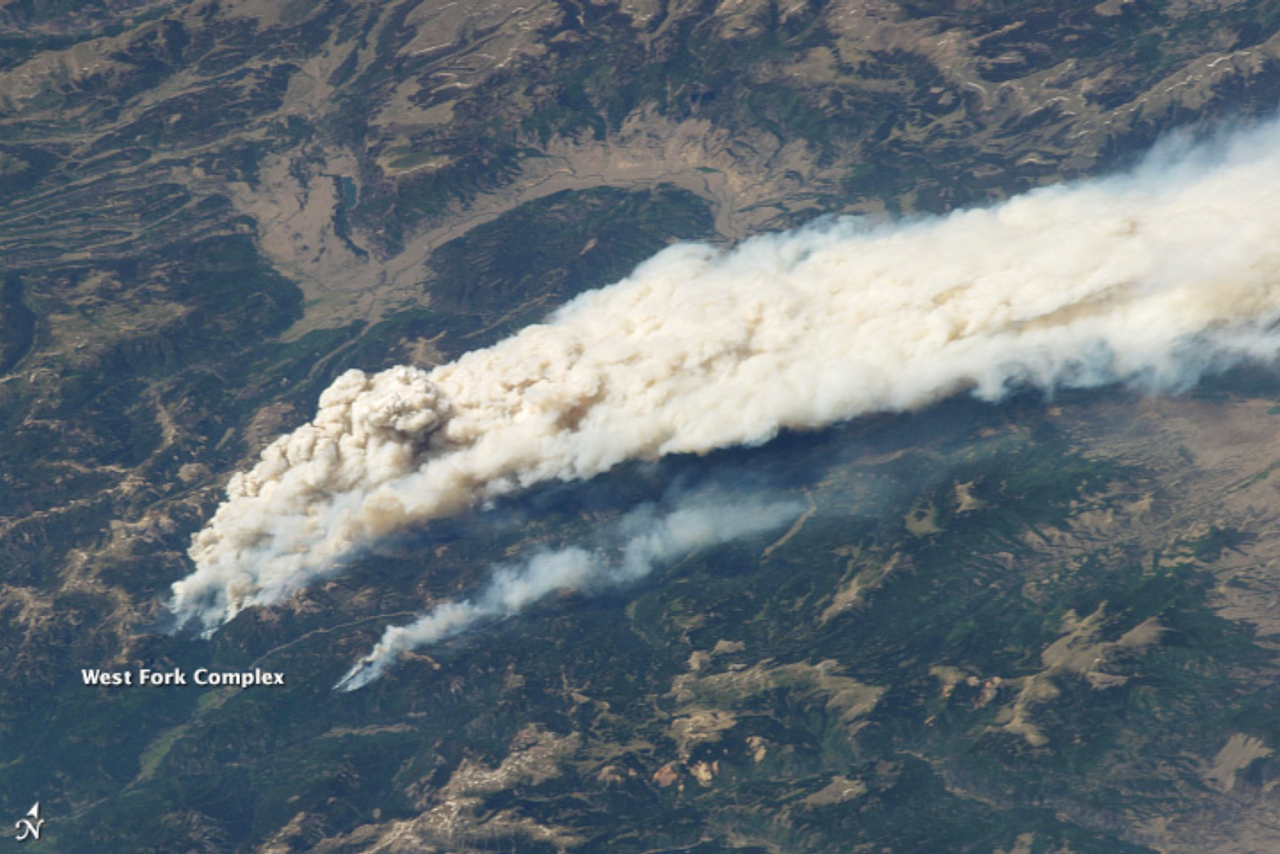
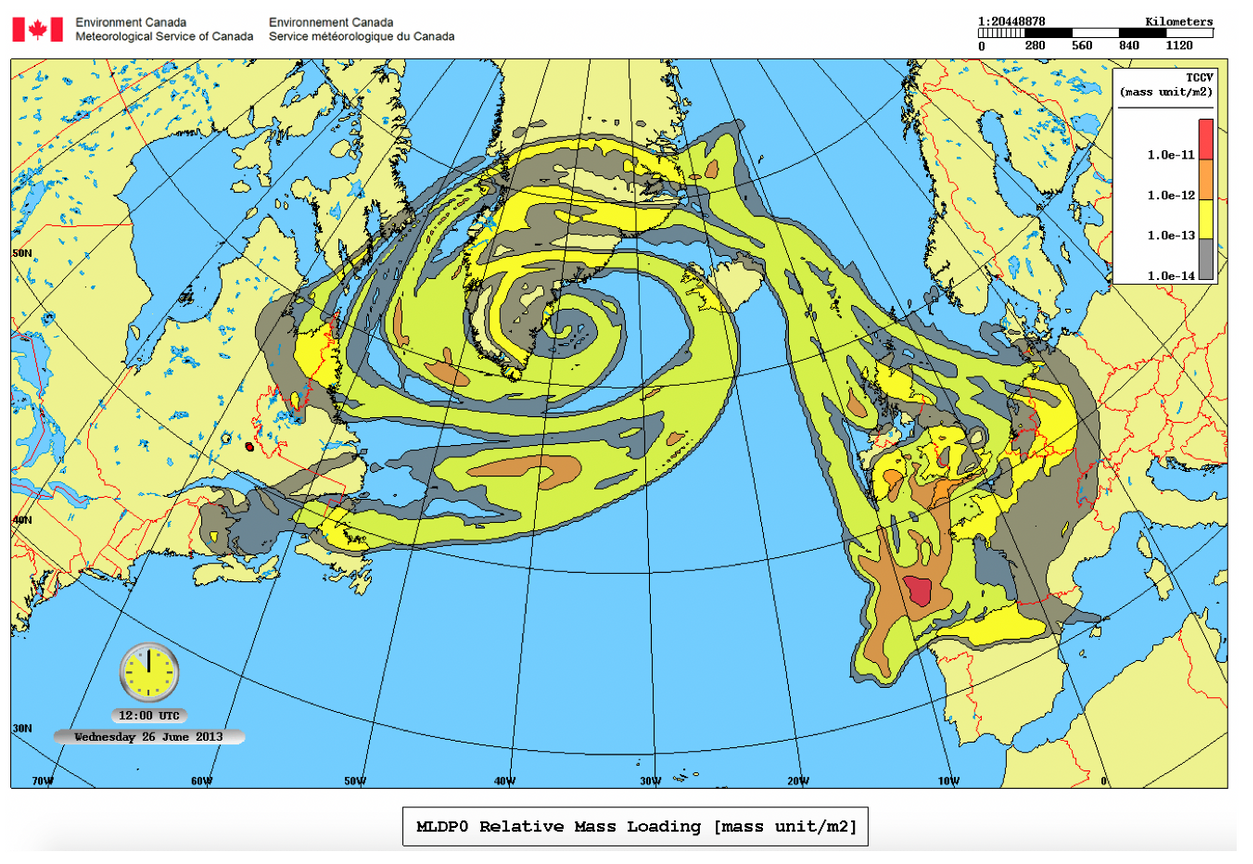
Above, the left image is of a wildfire producing so much smoke that it became a pyrocumulous cloud system. The right image shows how smoke can be trapped in a swirling cloud system and travel great distances (the fire began in Canada and some
of the smoke even travelled from Colorado).
Wildfires can cause thunderstorms (and vice versa), producing pyrocumulous and pyrocumulonimbus clouds. These are clouds that are often seen over volcanoes and fires and carry ash or smoke through the atmosphere. (7)
These convective systems carry smoke parallel to Earth’s surface as well as vertically through Earth’s atmosphere. There has been recent research on how natural hazards like volcanoes cause these convective systems, how these events
impact the lower stratosphere with smoke injections, and how smoke travels at different points in the atmosphere. (8) Past research on wildfires and the atmosphere has focused on the impact on Earth’s climate but has rarely touched on
what occurs in the near space environment as a result of large surface fires. Natural hazards such as wildfires may have an influence on the middle atmosphere and near space environment. The research of natural hazards such as wildfires
and the impact on stratospheric gravity waves has not been thoroughly investigated yet, despite the indication of a possible correlation between the two events. Gravity waves (also known as buoyancy waves) transport momentum and energy
from the lower atmosphere to the upper atmosphere and near space environment, and play an important role in influencing dynamics in these regions.
For further information, view my research on the topic: