With the many uses and applications of nuclear physics, there are also some concerns from use of nuclear energy, primarily safety and containment of nuclear waste. Use of nuclear power is primarily safe, and there have been few major reactor accidents in the history of civil nuclear power. In the event though of an unlikely accident, the outcome can be quite detrimental as seen notably by the Chernobyl and Fukushima Daiichi accidents.
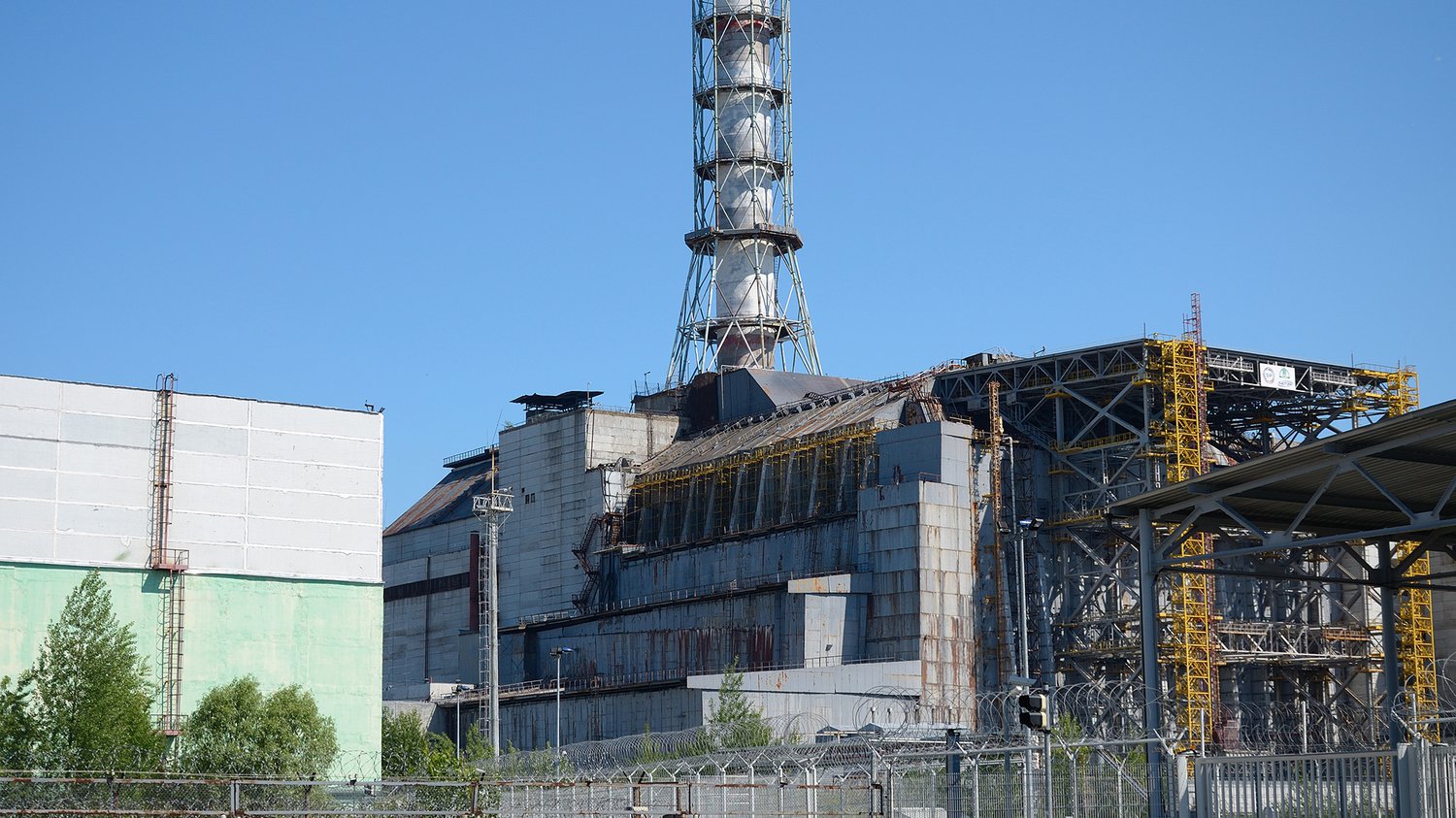

Photo of the Chernobyl nuclear reactor. Photo used from www.pbs.org
Disposal of nuclear waste:
The use of nuclear power plants as well as other applications such as production of nuclear weapons can generate a lot of nuclear waste, which must be disposed of in a safe and effective way. There are three main types of nuclear waste that are disposed of based on risk to human health and environment. These include high-level, transuranic, and low-level waste.
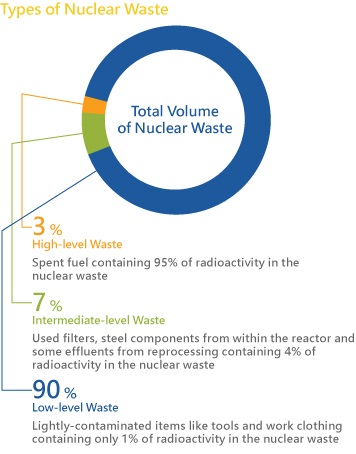
Amounts of different kinds of nuclear waste. Photo used from www.world-nuclear.org
Used nuclear fuel is either initially stored in wet or dry storage facilities, before it is either recycled or disposed of. This allows time for the waste to be cooled and the radioactivity to diminish slightly. One approach taken by some countries is to recycle the nuclear waste, as much of it can often be used again as fuel for certain types of reactors. This generally focuses on extracting substances such as uranium and plutonium. Another approach used is direct disposal, in which the fuel is disposed of in an underground repository. The fuel is placed in canisters and then sealed with rocks and clay. Waste from recycling is also placed in repositories.
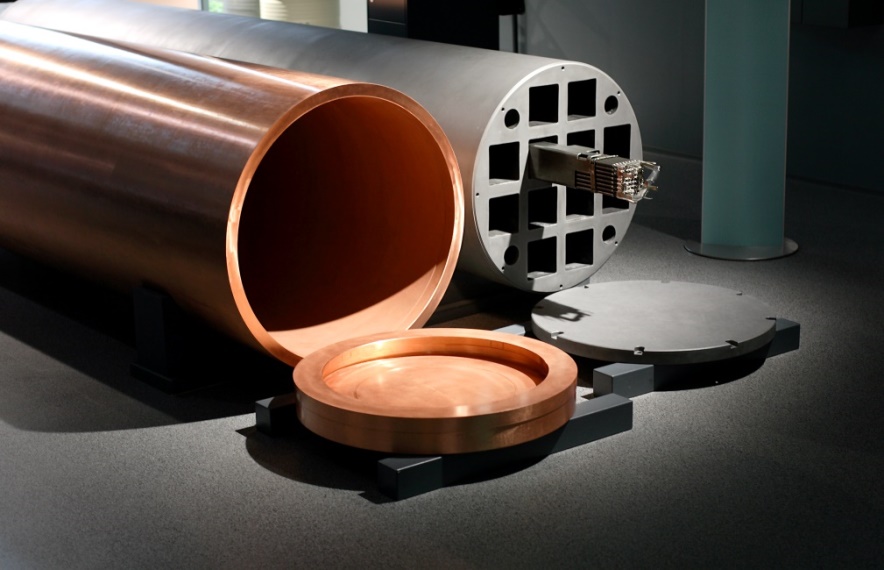

Example of containment canister used to store nuclear fuel. Photo used from www.world-nuclear.org