Aerodynamic Forces on Soccer Ball
Drag Coefficient (CD) and Drag

(FD -
air drag [N]; ρ - air density
[kg/m^3]; V - wind velocity [m/s]; A - projected
frontal area of the ball [m^2])
The aerodynamic drag
coefficient is a non-dimensional parameter that is
used to test the aerodynamic abilities of a ball.
It helps to determine the effect that airflow has
on a ball. Cd can
be then plotted versus Reynolds number and the
values compared with the values from testing a
different ball.
Reynolds number: (r - radius of
the ball [m]; μ - dynamic
viscosity of the air [kg/m*s]
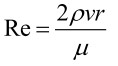
Drag is the air resistance to
the motion of the ball as it moves through the air. Drag
force is directed along and opposed the flight direction.
Drag depends on the shape and size of the ball. The
smoother the ball the less air drag. As stitches are used
to keep the soccer balls together the surface is never
truly smooth.
Weight
W = m*g [N]
(m - mass of the ball in kg; g = 9.81 m/s^2)
Weight is a force that is always
directed towards the center of the earth. For soccer ball
weight is mostly dependent on the mass of the ball. As the
ball is inflated with high pressure air, most of the mass
comes from the outside of the ball. In flight, the ball
rotates around its center of gravity which for a ball is
the geometrical center.
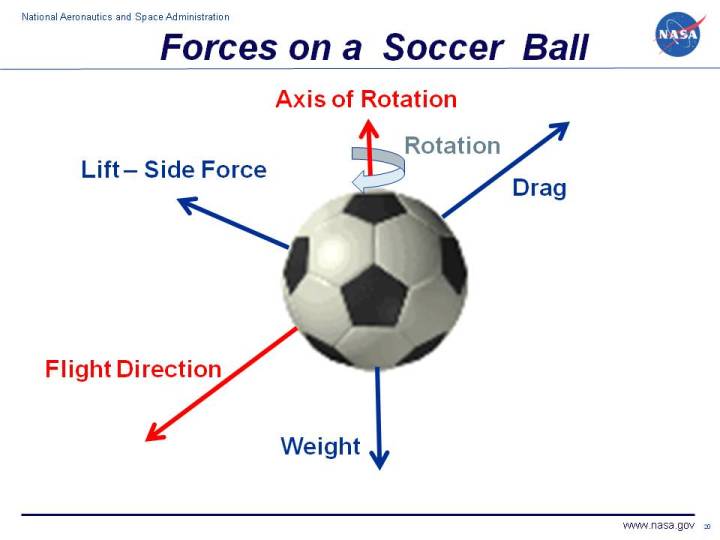
Illustrative image showing the forces acting on a ball in flight from www.grc.nasa.gov/www/k-12/airplane/socforce.html.
Side Force Coefficient (Cs)

The side force coefficient is also known as the lift coefficient is a perpendicular component of aerodynamic force to the flight direction. It is created by spinning the ball. The magnitude depends on the speed of rotation which can be varied by the way the player kicks the ball.
Spinning parameter (Sp)

(ω - rotational velocity [rad/s]; r -
radius of the ball [m]; v - wind speed [m/s])
Spinning parameter is a
coefficient that determines the balls ability to
spin during the flight and on the ground. By
increasing the spinning coefficient, the side force
increases too.