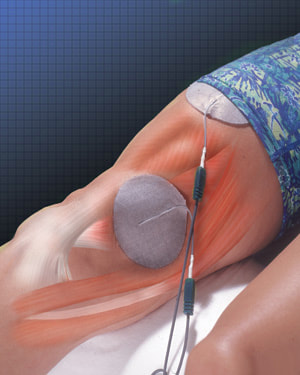
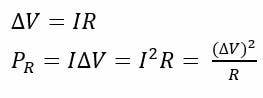Electrical StimulationElectrical current causes a muscle or a muscle group to contract. Contracting the muscle helps strengthen the affected muscle. Along with increasing muscle strength, the electrical current stimulation and the contraction of the muscle promotes blood supply to the area which ultimately assists in healing
Treats: osteoarthritis, fibromyalgia, back pain, muscle strains, ligament sprains, neck pain, tendinitis, bursitis |
Different Types of Electrical Stimulations
Transcutaneous Electrical Neuromuscular Stimulation (TENS)Applies electrodes to body over painful areas. The intensity of electricity is adjusted to block pain signals
|
IontophoresisAlong with electrical stimulation, there is also the administration of medication to decrease inflammation. Drugs can also be used to break up calcium deposits
|
Neuromuscular Electrical Stimulation (NMES)Causes single muscle/group to contract. It recruits other muscle fibers to react as a result.
|
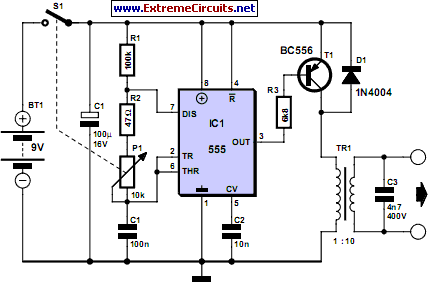
Electric CurrentAt least two pads are connected by wires to each channel. The user gets to control the intensity of the electrical current to each pair of pads.
The circuit inside a TENS machine can be programmable to generate pulses. These pulses can vary with current strength, pulse rate and pulse widths. The current intensity 0 - 80 mA, with some machines allowing up to 100mA. A conventional TENS uses a frequency of 40-150Hz with a pulses during of 50 microseconds at maximum. |
Battery = source of potential difference
Current = motion of charges sustained by an electric field
Current = motion of charges sustained by an electric field