The 7 Detectors
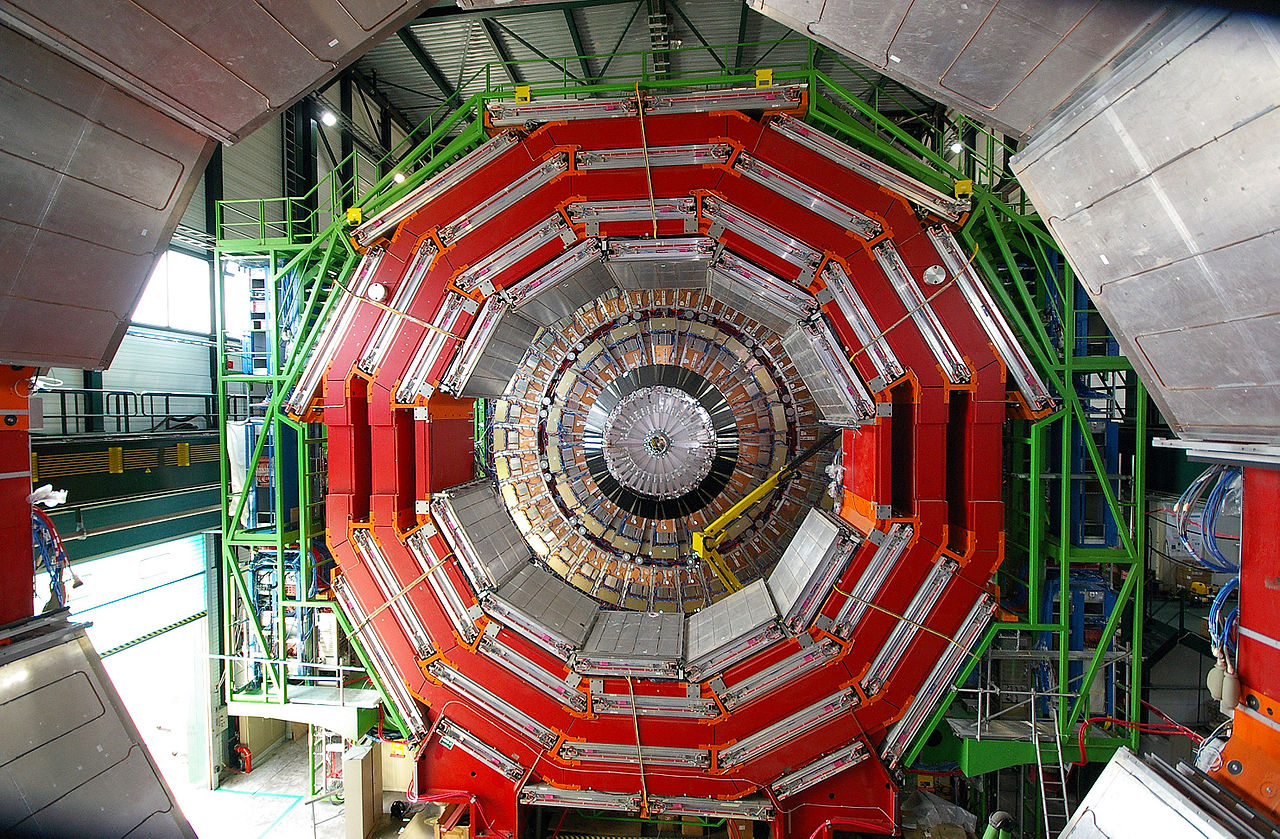
The CMS (Compact Muon Solenoid)
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Compact_Muon_Solenoid#/media/File:CMS_Under_Construction_Apr_05.jpg
The CMS investigates a wide range of physics. It
is 22m long, 15m in diameter, and weighs 14,000 tones. This
experiment's goal is to search for the Higgs boson, other
dimensions, and dark matter.
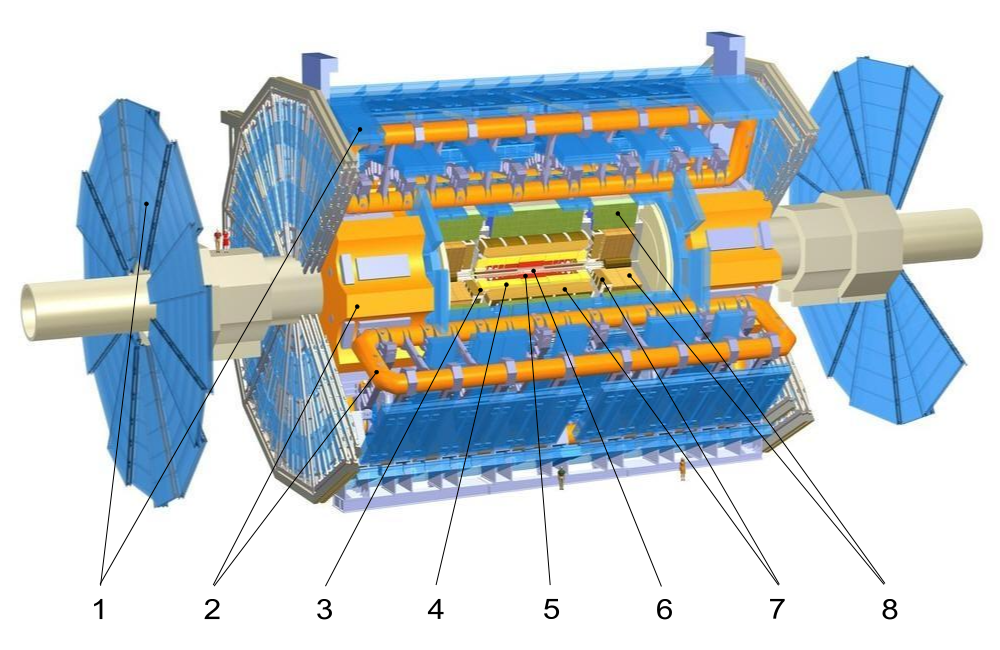
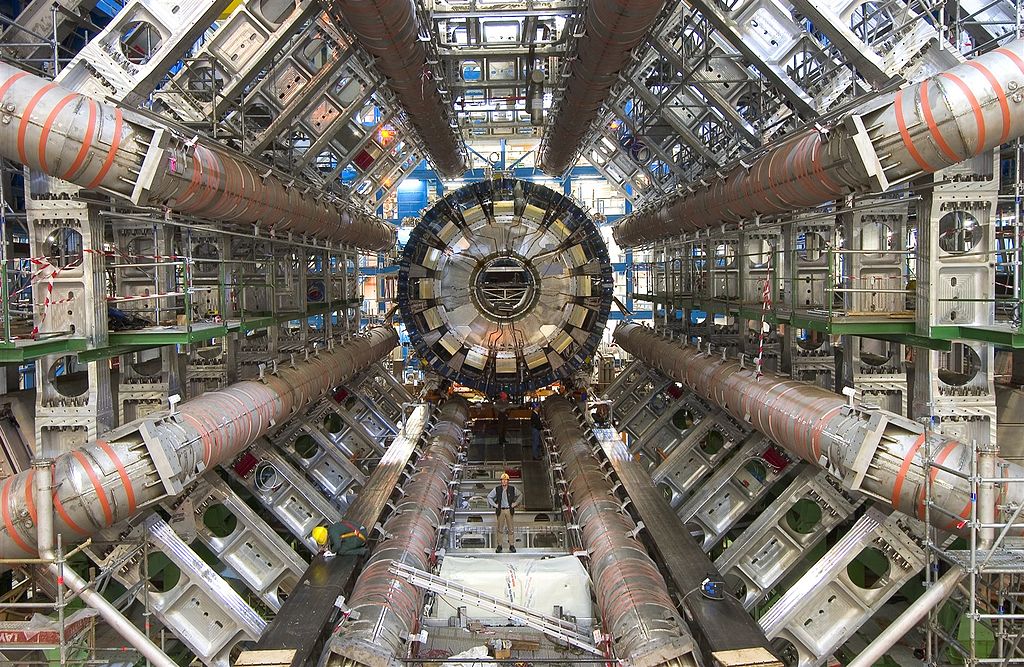
The ATLAS

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ATLAS_experiment#/media/File:ATLAS_Drawing_with_Labels.svg
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ATLAS_experiment#/media/File:Installing_the_ATLAS_Calorimeter.jpg
This machine is 46m long, 25m in diameter and weight 7,000
tonnes. This experiment's job is to observe phenomena among
massive particles such as lead collide.
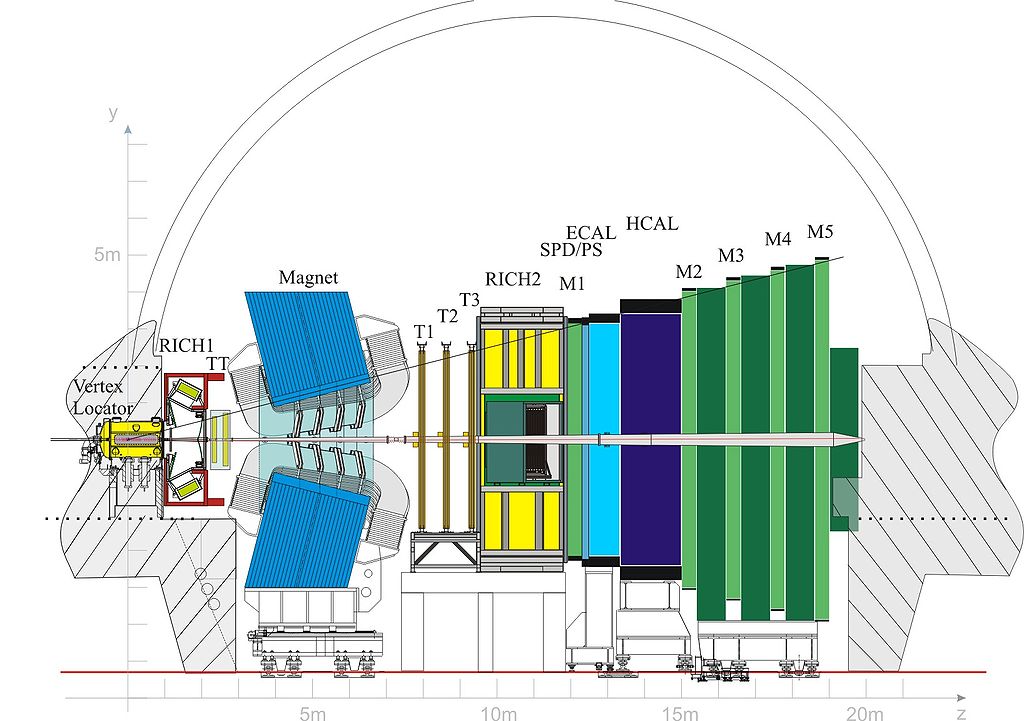
The LHCb
https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LHCb_experiment#/media/File:Lhcbview.jpg
The LHCb's duty is to perform cross sectional measurements
in the forward direction to help explain the
matter-antimatter asymmetry.
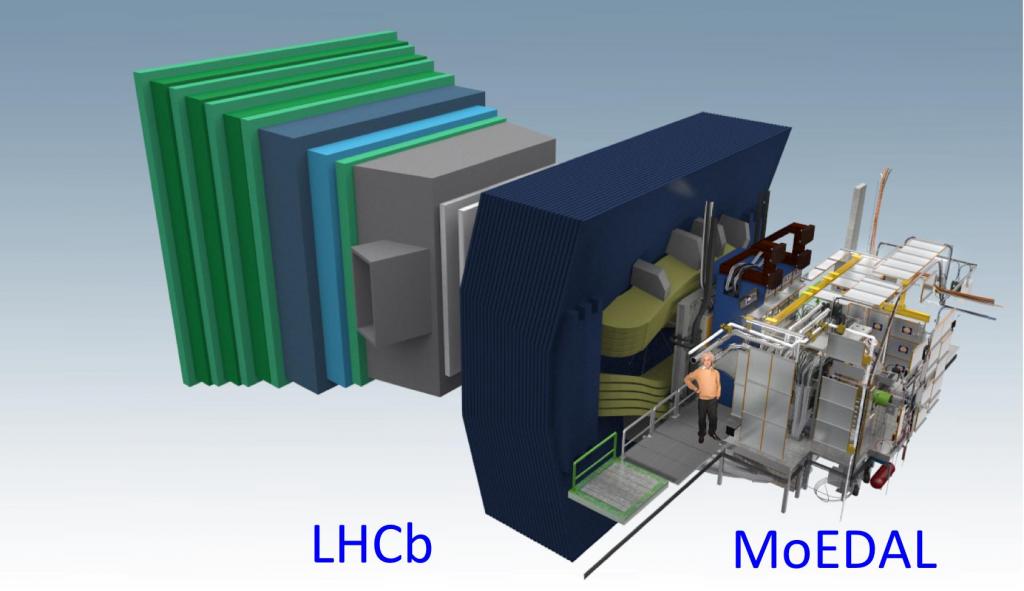
The MoEDAL
http://moedal.web.cern.ch/
This experiment uses nuclear track detectors (which suffer
damage due to highly ionized particles) to find the magnetic
dipole and pseudo-stable particles.
The TOTEM
http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/science/nature/7534869.stm
This device measures elastic scattering, diffraction and
cross section of the particle beams.
The LHCf

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/LHCf_experiment#/media/File:LHCf.jpg
The LHCf (placed on both sides of ATLAS) observes
cosmic ray physics in the forward region of each
collision and will hopefully explain the origin of
ultra-high-energy cosmic rays.
The ALICE

https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/ALICE_experiment
The ALICE focuses on the physics of strongly
interacting matter at extreme energy densities. The
energy densities here are great enough to produce a
plasma where quarks and gluons are separate. The
reverse of this transition is believed to play a
role in the collapsing of neutron stars and other
objects.
<---- ---->








