Overview
home
What is the higgs boson?
The Higgs Boson is first and
foremost an elementary 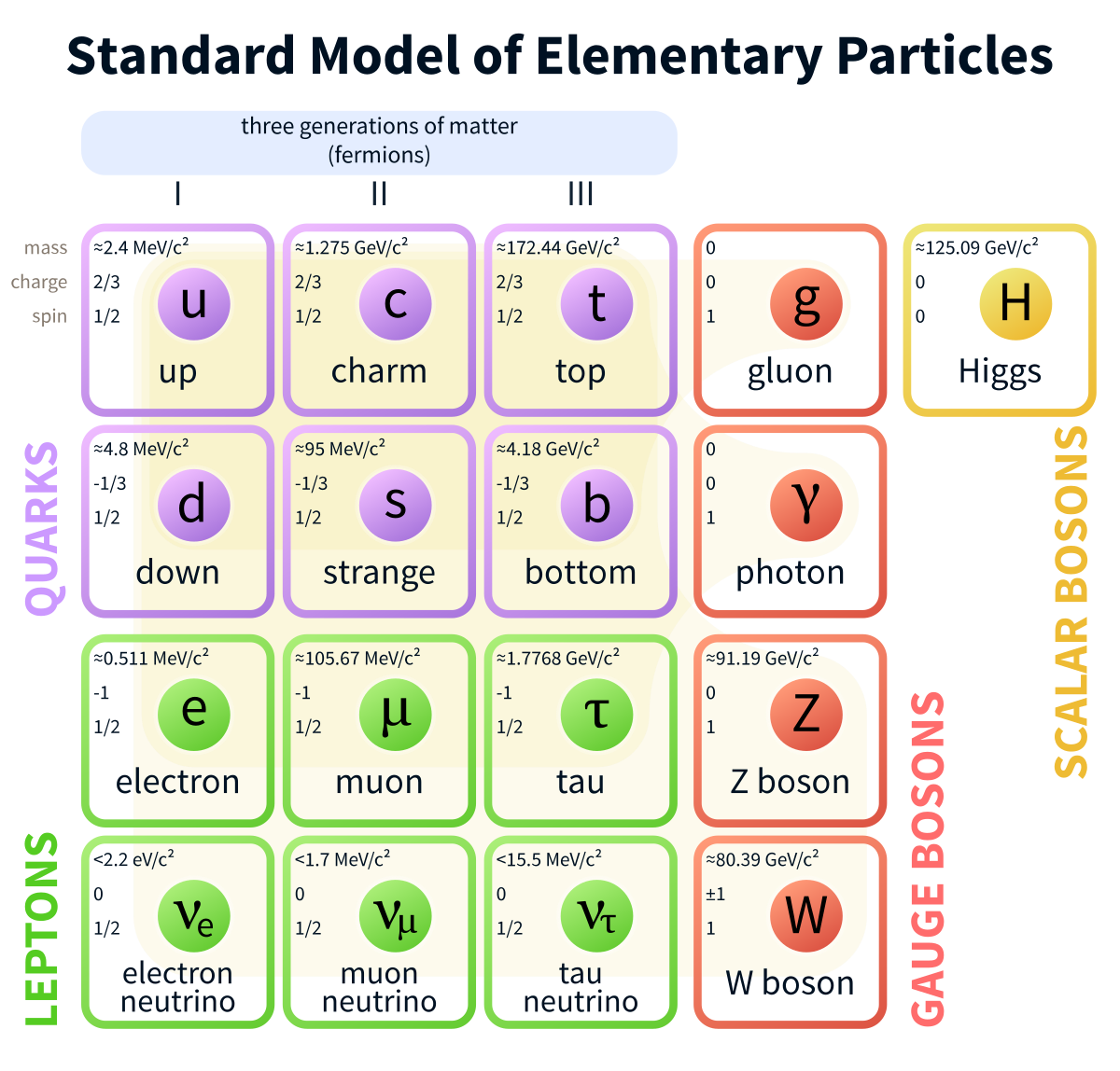 particle. An elementary particle is something that cannot be broken
down any further like
electrons. So in
other words they are building blocks for other particles just like
electrons are building blocks for atoms. It is
important to keep in mind that the Higgs Boson is far
smaller than electrons which is one of the reasons
that it was so hard to find. In addition the Higgs
Boson is obviously a boson given its name, but what
exactly is a boson. A boson is
part of one of two categories of elementary particles,
the other being fermions. While fermions carry the
mass of objects, bosons carry the forces of the same
objects. But the Higgs Boson is slightly different
from other bosons because it is a "scalar boson"
meaning that it interacts with other bosons to give
them their traits. For the Higgs Boson in particular,
which is the only scalar boson, it gives the W and Z
bosons their mass through an interaction with the
Higgs Field. The W and Z bosons are the force
carriers that control the weak force, one of four
types of forces in physics.
particle. An elementary particle is something that cannot be broken
down any further like
electrons. So in
other words they are building blocks for other particles just like
electrons are building blocks for atoms. It is
important to keep in mind that the Higgs Boson is far
smaller than electrons which is one of the reasons
that it was so hard to find. In addition the Higgs
Boson is obviously a boson given its name, but what
exactly is a boson. A boson is
part of one of two categories of elementary particles,
the other being fermions. While fermions carry the
mass of objects, bosons carry the forces of the same
objects. But the Higgs Boson is slightly different
from other bosons because it is a "scalar boson"
meaning that it interacts with other bosons to give
them their traits. For the Higgs Boson in particular,
which is the only scalar boson, it gives the W and Z
bosons their mass through an interaction with the
Higgs Field. The W and Z bosons are the force
carriers that control the weak force, one of four
types of forces in physics.Where did it come from?
As
previously mentioned,
the Higgs Boson is an excitation of the Higgs Field.
But what exactly is a Higgs Field and what
does an excitation of it mean? We can use the
analogy of dropping a a golf ball into a lake to help us
understand what these terms mean. Let us
consider the golf ball as an elementary
particle, such as the W and Z bosons that I discussed earlier,
and the lake as the Higgs Field. When you drop the
golf ball in the water it creates a splash. That
splash is what would be the Higgs Boson in this
analogy. Just like the splash is and excitation of the
lake, the Higgs Boson is an excitation of the water.
But what exactly is the Higgs Field? The Higgs field
it what gives elementary particles their mass and is
omnipresent throughout the entire universe. This
concept is discussed in the implications section.
excitation of the Higgs Field.
But what exactly is a Higgs Field and what
does an excitation of it mean? We can use the
analogy of dropping a a golf ball into a lake to help us
understand what these terms mean. Let us
consider the golf ball as an elementary
particle, such as the W and Z bosons that I discussed earlier,
and the lake as the Higgs Field. When you drop the
golf ball in the water it creates a splash. That
splash is what would be the Higgs Boson in this
analogy. Just like the splash is and excitation of the
lake, the Higgs Boson is an excitation of the water.
But what exactly is the Higgs Field? The Higgs field
it what gives elementary particles their mass and is
omnipresent throughout the entire universe. This
concept is discussed in the implications section.
 excitation of the Higgs Field.
But what exactly is a Higgs Field and what
does an excitation of it mean? We can use the
analogy of dropping a a golf ball into a lake to help us
understand what these terms mean. Let us
consider the golf ball as an elementary
particle, such as the W and Z bosons that I discussed earlier,
and the lake as the Higgs Field. When you drop the
golf ball in the water it creates a splash. That
splash is what would be the Higgs Boson in this
analogy. Just like the splash is and excitation of the
lake, the Higgs Boson is an excitation of the water.
But what exactly is the Higgs Field? The Higgs field
it what gives elementary particles their mass and is
omnipresent throughout the entire universe. This
concept is discussed in the implications section.
excitation of the Higgs Field.
But what exactly is a Higgs Field and what
does an excitation of it mean? We can use the
analogy of dropping a a golf ball into a lake to help us
understand what these terms mean. Let us
consider the golf ball as an elementary
particle, such as the W and Z bosons that I discussed earlier,
and the lake as the Higgs Field. When you drop the
golf ball in the water it creates a splash. That
splash is what would be the Higgs Boson in this
analogy. Just like the splash is and excitation of the
lake, the Higgs Boson is an excitation of the water.
But what exactly is the Higgs Field? The Higgs field
it what gives elementary particles their mass and is
omnipresent throughout the entire universe. This
concept is discussed in the implications section.