There are two types of electrical transformers: step-up and step-down transformers. The main function of a transformer is to convert high voltage to low voltage or vice versa. Converting high voltage to low voltage is called step-down and the other way around uses a step-up transformer.
A typical pole transformer
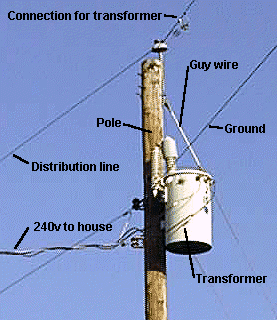 The transformer in this photo is considered to be a
step-down type.
The transformer in this photo is considered to be a
step-down type.This pole transformer converts high voltages from electrical power plants that is around 7,200 voltage down to voltages between 120 and 240. It has 3 wires coming out of it's output and heading into a house with a voltage ranging from 120 to 240. These 3 wires are called the hot, the neutral, and the grounded wire. The hot wire is coated in black which carries the potential difference (Voltage). The white wire is consider to be the neutral wire, which carries the current back into the system and the grounded wire is a backup for the system.
http://science.howstuffworks.com/environmental/energy
/power9.htm
When the current is too strong in the output of the electric transformer, the surplus amount of electrons will flow though to ground and discharge into the ground.
How Electrical Transformers Work?
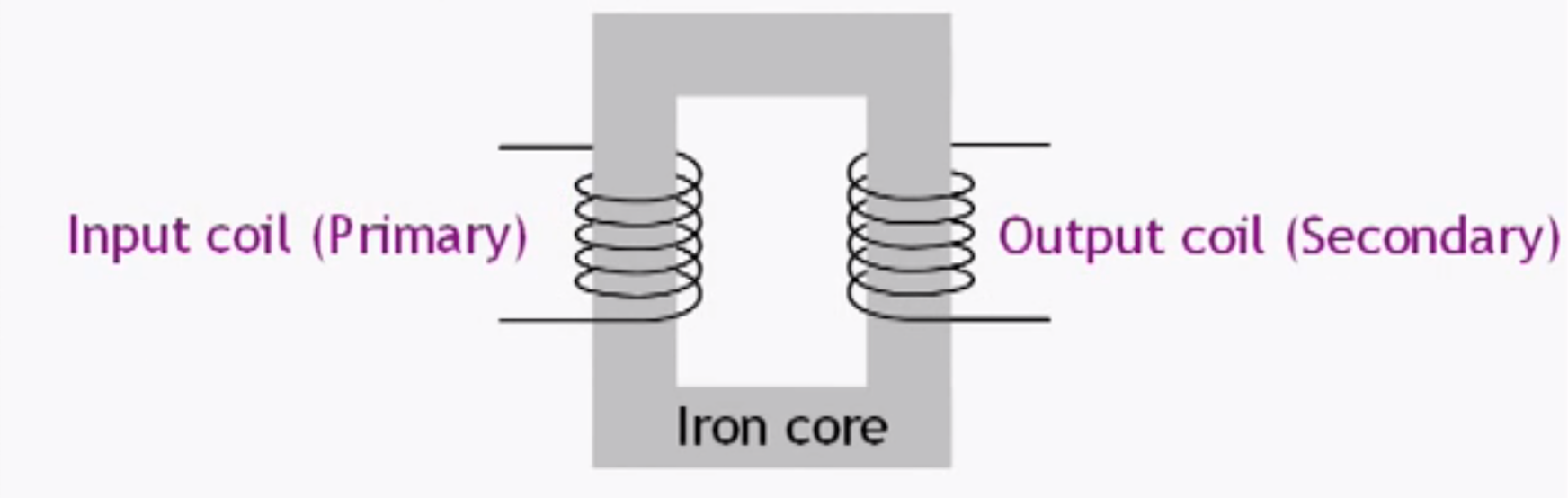
Inside a transformer there is an iron core, an input coil (Primary), and an output coil (Secondary).
Electrical transformers have two concepts
1. Electromagnetism-
"Making magnetism by using electrical current"
2. Electromagnetic Induction-
"Creating an electrical current using magnetism"
Inside A Electrical Transformer
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZjwzpoCiF8A
With the photo below I will explain how electromagnetic induction and electromagnetism cause either a voltage drop or increase. On the primary side, we have current and voltage going through the coils which increase the magnetic field on the secondary coil side. This happens because electromagnetism is being created by the increase or decrease of current and voltage and by also using a lot of coils that are wrapped around the input coil. This electromagnetism created on the primary coil has an effect on the secondary side which is called electromagnetic induction. Electromagnetic induction only occurs when the primary side has an increase or decrease in current and voltage. When electromagnetic induction occurs because of the electromagnetism, there is an induced voltage in the secondary coil.
Ultimately, the induced voltage strength depends on the strength of the magnetic field and the number of coils in the output coil.
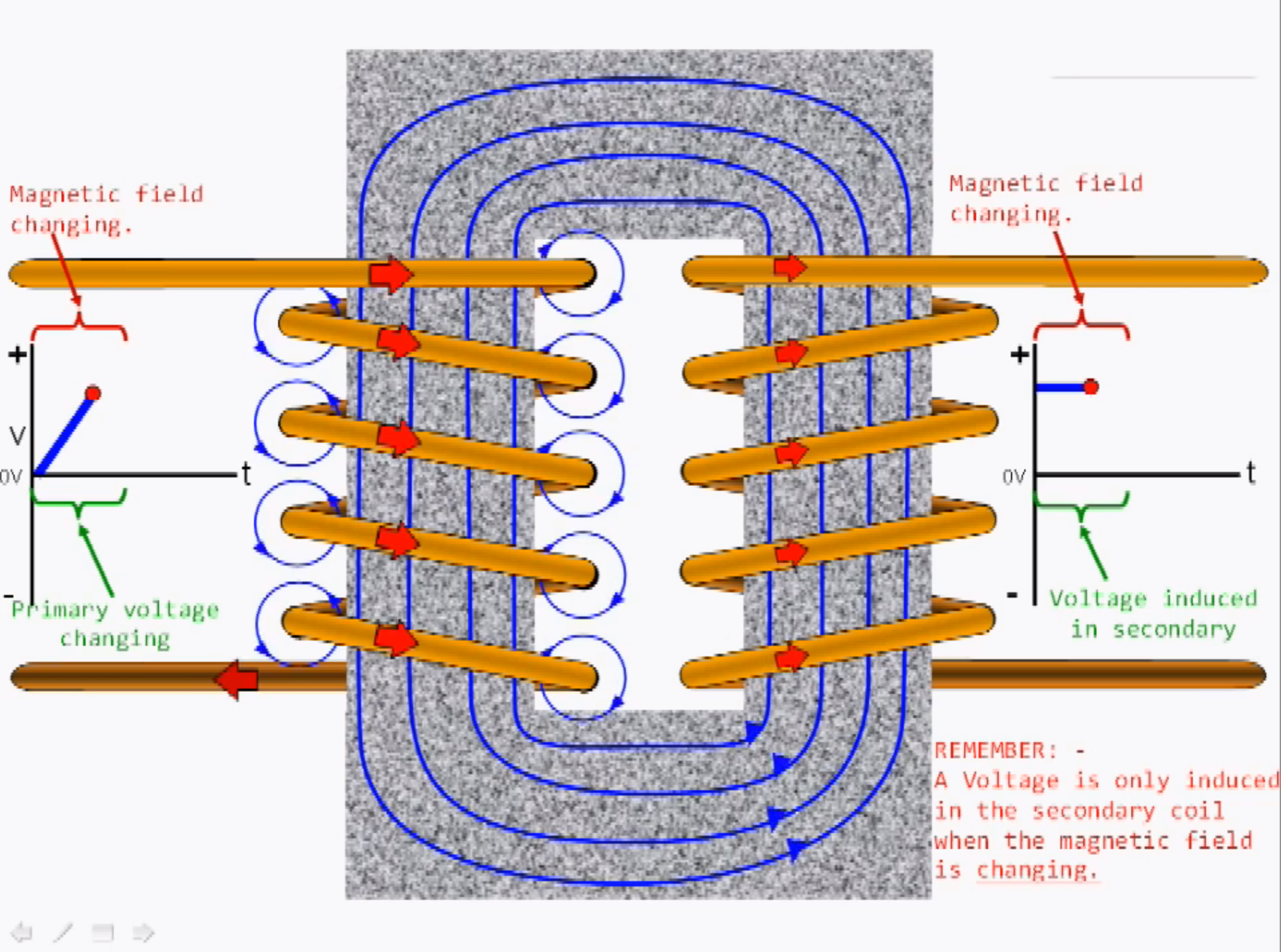
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ZjwzpoCiF8A
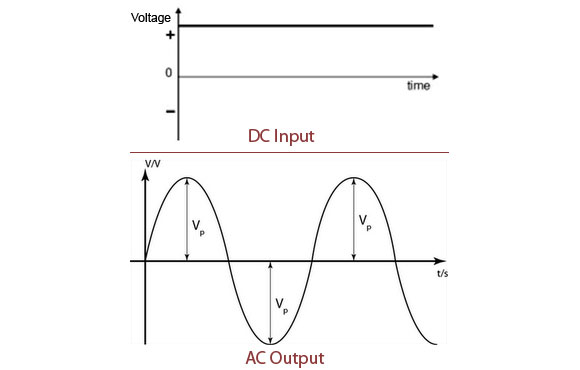
In order to get the primary coil to have a constant increase or decrease in current and voltage you will need to have an Alternating Current (AC) power and not a Direct Current (DC) power source. This is because Direct Current only supplies a constant voltage. Thus no magnetic field will be created and no induced voltage will be found in the secondary coil.
Alternating Current (AC)- is when there is a constant increase and decrease of Voltage over time like a sine wave. AC moves in a periodically reversed direction. AC is usually found in over head electrical wires coming from electrical power plants.
Direct Current (DC)- is when there is a constant flow of voltage over time in a circuit and only moves in one direction. DC are usually found in small circuits. (An example would be a light bulb wired in a closed series with a battery.)
Direct Current On Top &
Alternating Current On Bottom
http://cleangreenenergyzone.com/wp-content/uploads/2011/06/dc-to-
ac-inverter.jpg
Relationship Between The Primary and Secondary
Voltage (Secondary) = Coil Turns (Secondary)
Voltage (Primary) Coil Turns (Primary)
By looking at the relationship, a step-up transformer will have more coils on the primary side and a step-down transformer will have more coils on the secondary side.