Sensors
This page explains how the many sensors of a
polygraph work.
Breathing Rate

thoughttechnology.com
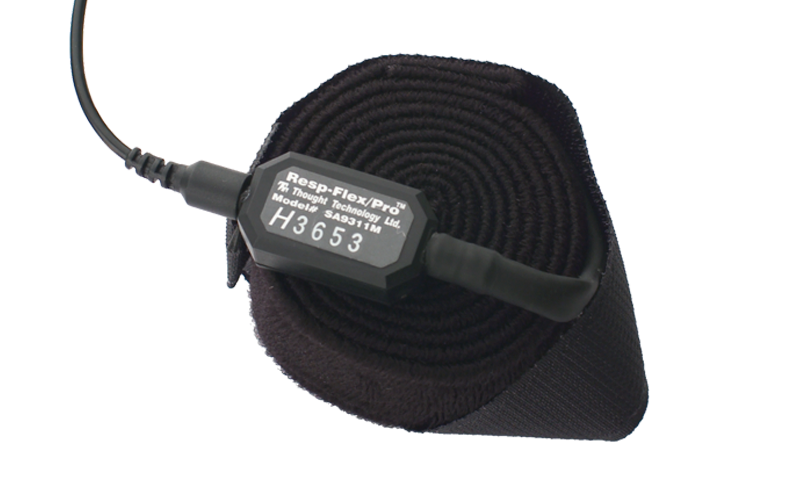
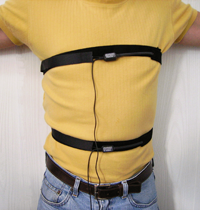
The most common way to measure the breathing
rate of a person is a respiration sensor. Respiration sensors
generally consist of a band that wraps around the subjects
chest, an elastic strap, and a pressure sensor. As the subject
breaths in, his/her chest expands, the rubber strap stretches
out, the pressure sensor reads a higher value. Generally, a
pressure sensor has a voltage applied over it in series with a
resistor. As the pressure sensor feels more pressure, it
becomes more resistive. As it does this, more voltage drops
across the resistor, where the output voltage is read. While
the output voltage is at its highest value, the subject's
chest is fully inflated. While the output voltage is at its
lowest value, the subject's chest is fully deflated. As the
subject breaths, this creates a waveform; the period of the
waveform can be used to determine the breathing rate of the
subject (Respiration Sensor).
Heartbeat Rate

thoughttechnology.com
There are two commonly used types of sensors
for measuring the heart-rate of a person. The first is the
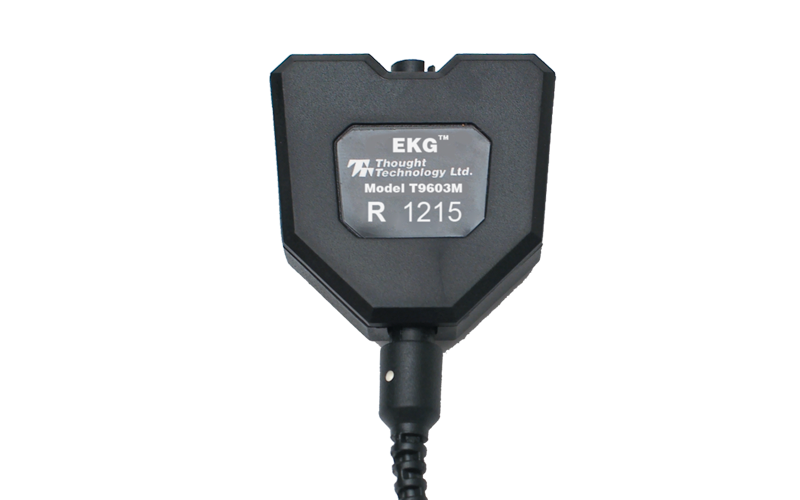
electrocardiography (ECG or EKG) sensor. This is the type of
sensor they use to measure a person's vital sign's in a
hospital. It is an electrocardiograph sensor or pre-amplifier,
for directly measuring the heart's electrical activity. It
amplifies the small electrical voltage that is generated by
the heart muscle when it contracts. The sensor works by
attaching two or more electrodes on opposite sides of a
person's heart that detect the tiny electrical changes on the
skin that arise from the heart muscle depolarizing during each
heartbeat. The time between each heartbeat can be used to
determine the subject's heart-rate (EKG Sensor).


thoughttechnology.com
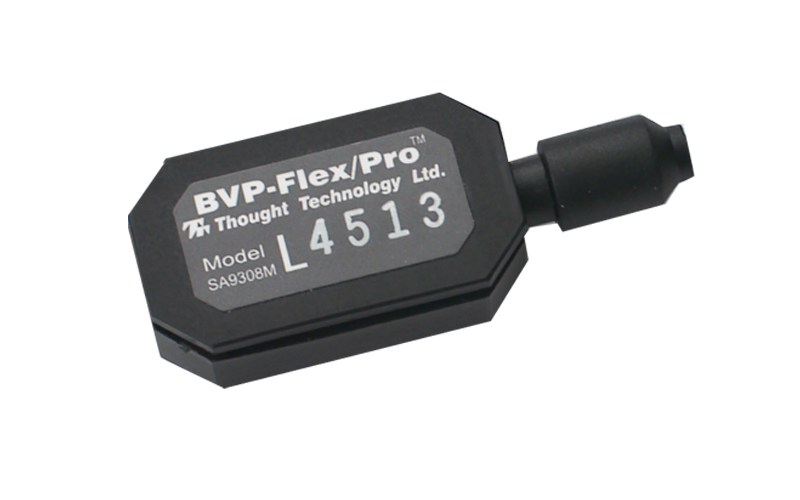
The other type of commonly used sensor for
measuring the heart rate of a person is the heart-rate
(HR)/blood volume pulse (BVP) sensor. This sensor works by
emitting light (usually infrared light) against the subject's
skin surface, and measuring the amount of light reflected back
at the sensor. During each heartbeat, there is more blood in
the skin. The blood changes the amount of light reflected back
at the sensor. When the heart isn't beating the skin's blood
level returns to normal. Time between each heartbeat can be
used to determine the subject's heart-rate (HR/BVP
Sensor).
Blood Pressure

inds.co.uk
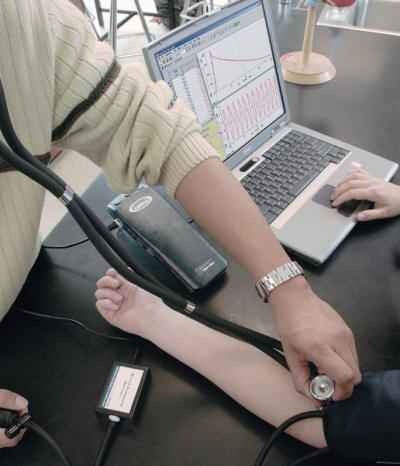
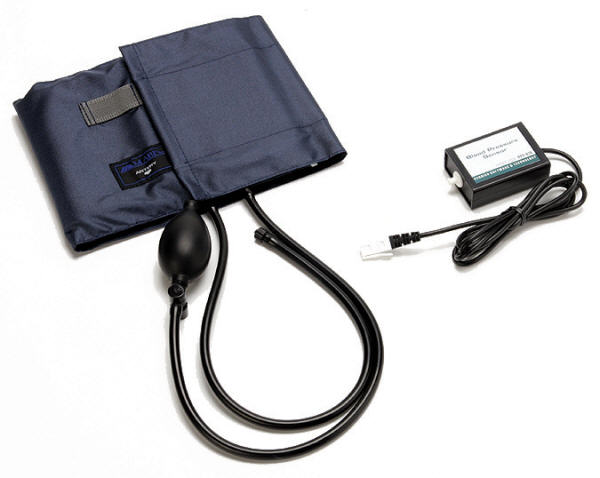
The most common way to measure the blood
pressure of a person is a blood pressure sensor (BPS). Blood
pressure sensors generally consist of an inflatable cuff that
is put around the subject's upper arm, a flexible membrane,
and a differential pressure sensor. The cuff is inflated to
ensure that the subjects arteries push up against the membrane
whenever his/her heart beats. When the subject's heart beats,
his/her arteries expand due to the increase in blood pressure.
As the subject's arteries expand, his/her arm tries to expand
as well, pushing up against the flexible membrane. As the
membrane flexes, the output voltage from the pressure sensor
varies similar to the pressure sensor that the respiration
sensor uses (Blood Pressure Sensor).
Perspiration


thoughttechnology.com
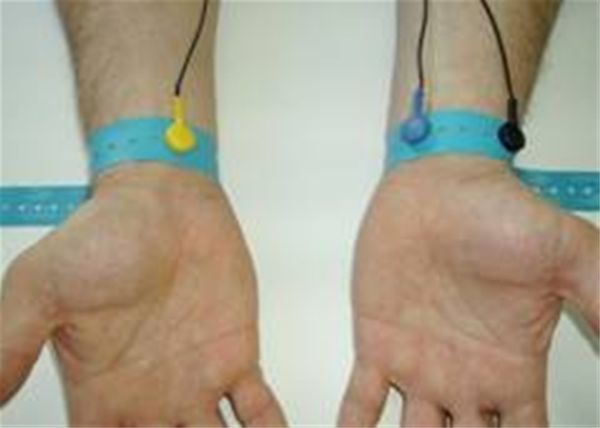
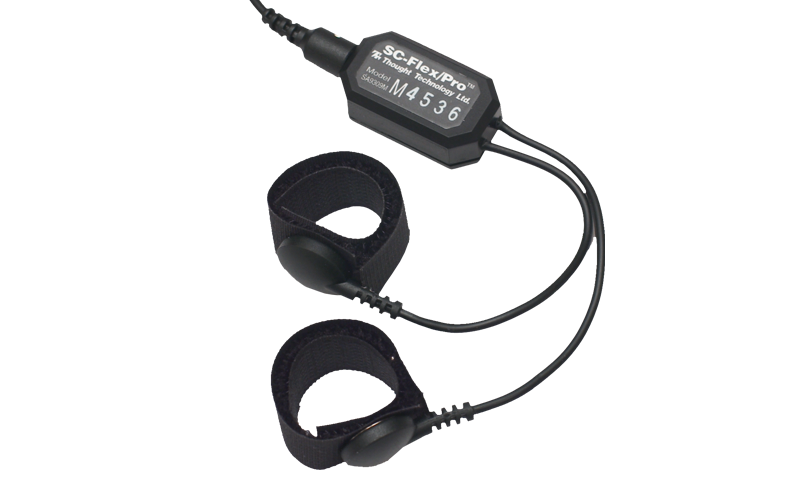
The easiest way to measure a person's
perspiration level is to test his/her skin conductivity. This
can be done with a skin conductivity sensor. Skin conductivity
sensors measure the electrical conductance between two points
on a person's skin. These two points are most often the
subject's fingers. These sensors work by wrapping a conductive
material around two of the subject's fingers, and attaching
probes to it. A voltage is then applied to the probes and
across the subjects hand. If the subject is perspiring,
his/her sweat will fill in air gaps between his/her fingers
and the conductive material. This will lower the total
resistance of the subject's hand. The sensor will determine
the conductance of the subject's hand similar to how pressure
sensors do, and the output voltage can be used to determine
how much the subject is perspiring (Skin Conductance Sensor).