Subduction
Zone Seismicity
Seismicity refers to the geographic and historical distribution of
earthquakes. Subduction zone seismicity clearly refers to seismic
activity along subduction zones. Earthquakes occurring along
subduction zones are of particular interest because they can
generate very shallow and hence horribly destructive earthquakes. As
described before, the dense oceanic plate will subduct beneath the
more buoyant continental plate and as the two plates slide past each
other, frictional forces build and are released in the form of
earthquakes. Subduction zone earthquakes are particularly
interesting because one can actually map the depth of the
earthquakes occurring as the plate is descending back into the
asthenosphere. By mapping the depth and location of subduction zone
earthquakes, the actual structure of the subduction zone can be
identified, such as how steeply the plate is dipping below the
other.
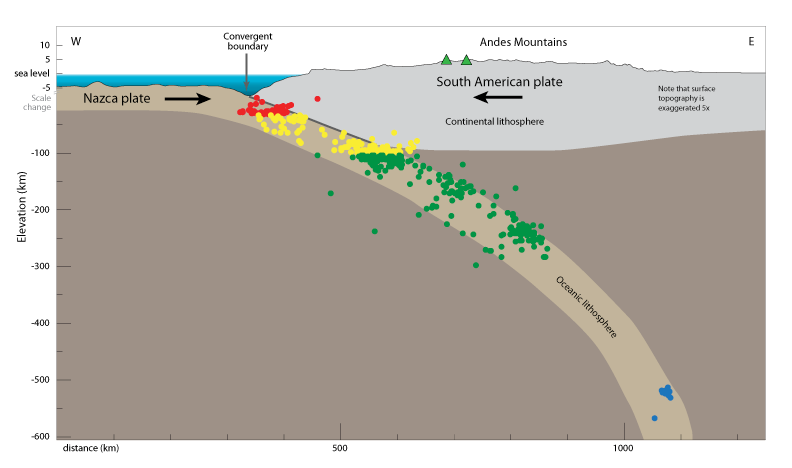
Fig 17. A plot of earthquakes along
a subduction zone. Red is shallow, yellow is intermediate, green
is deep.
"Visionlearning.com." Visionlearning. N.p., n.d. Web. 11 Apr. 2015.
<http://www.visionlearning.com/en/library/Earth-Science/6/
Plates-Plate-Boundaries-and-Driving-Forces/66>.
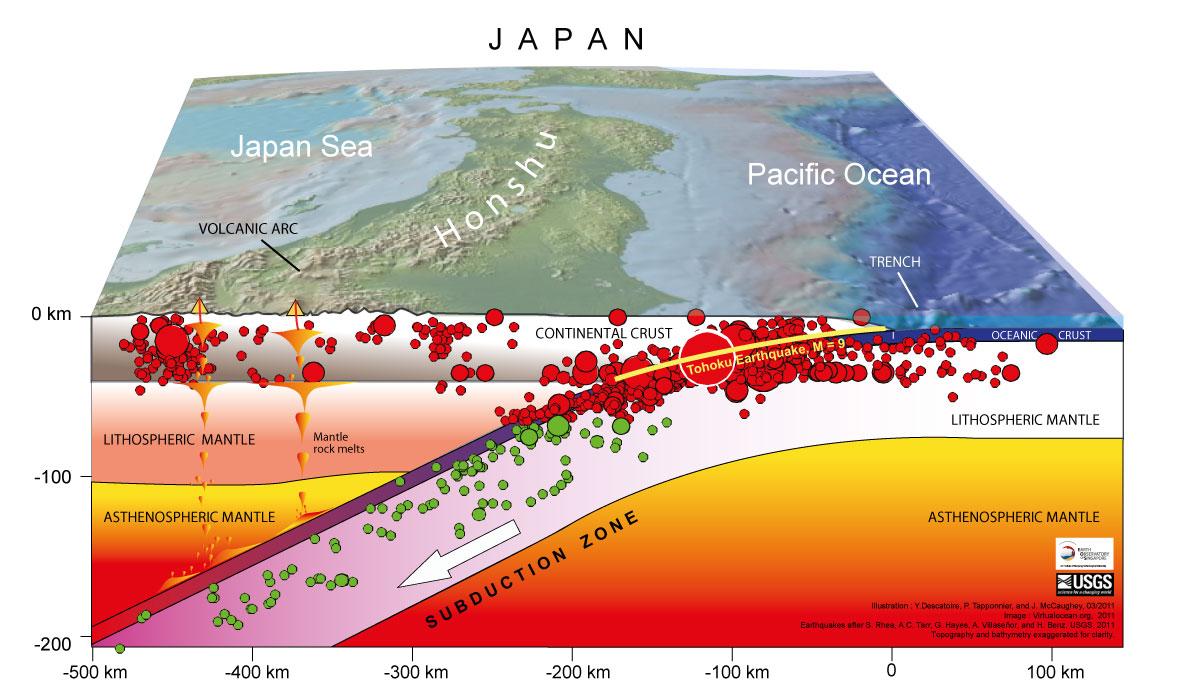
Fig 18. Subduction zone earthquakes plotted along the
Pacific Plate and Eurasia Plate boundary. The Tohoku earthquake
is clearly the largest plot at a magnitude of 9. This earthquake
took place about 45 miles east of Tohoku at a depth of about 20
miles below the surface. Shortly after the 6 minute long quake,
was a large tsunami that caused enormous damage.
"The Great East Japan (Tohoku)
2011 Earthquake: Important Lessons from Old Dirt." Earth
Observatory of Singapore. N.p., n.d.
Web. 11 Apr. 2015.
<http://www.earthobservatory.sg/news/great-east-japan-tohoku-2011-earthquake-important-lessons-old-dirt#.VTX6H9LBzGc>.
Subduction
Zone Seismicity in Alaska
The state of Alaska is located on a continental plate called the
North American Plate. The neighboring Pacific Plate is an oceanic
plate that is subducting beneath the North American Plate. The
entire southern part of Alaska, including the Aleutian Islands is
completely wrought with subduction zone earthquakes. In fact, the
second largest earthquake ever recorded occurred very near the city
of Anchorage Alaska on March 27 of 1964. It was a 9.2 magnitude
earthquake that lasted about 3 minutes and was followed by a very
devastating tsunami. These two events, together, caused damage in a
great deal of coastal Alaskan towns and 131 lives were lost.
Accompanying the earthquake was a great deal of vertical
displacement in many locations all across the state. Some of the
worst vertical displacements and landslides occurred in an area
called Turnagain Heights.

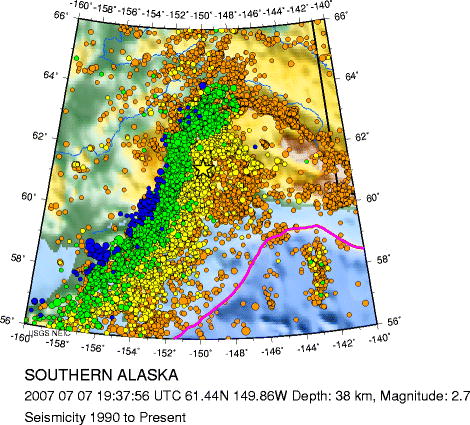
Fig 19. This image shows exactly where the Pacific Plate
is subducting beneath the North
American
Fig 20.
Subduction zone seismicity in Southern Alaska. Larger dots
correspond to larger
Plate. "Alaska
Tsunami Modeling Page." Alaska
Tsunami Modeling Page. N.p., n.d.
Web.
earthquakes. Orange dots are shallow earthquakes
approximately 0-35km deep.
19 Apr. 2015.
<http://www.aeic.alaska.edu/tsunami/>.
Blue
dots indicate much deeper earthquakes
- approximately 150-300 km below
the surface.
"Magnitude
2.7 SOUTHERN ALASKA." USGS
Earthquake Hazards Program:
Historic Seismicity: SOUTHERN ALASKA.
N.p., n.d. Web. 19 Apr. 2015.
<http://seisan.ird.nc/USGS/mirror/neic.usgs.gov/neis/bulletin/neic_eme2_h.html>.
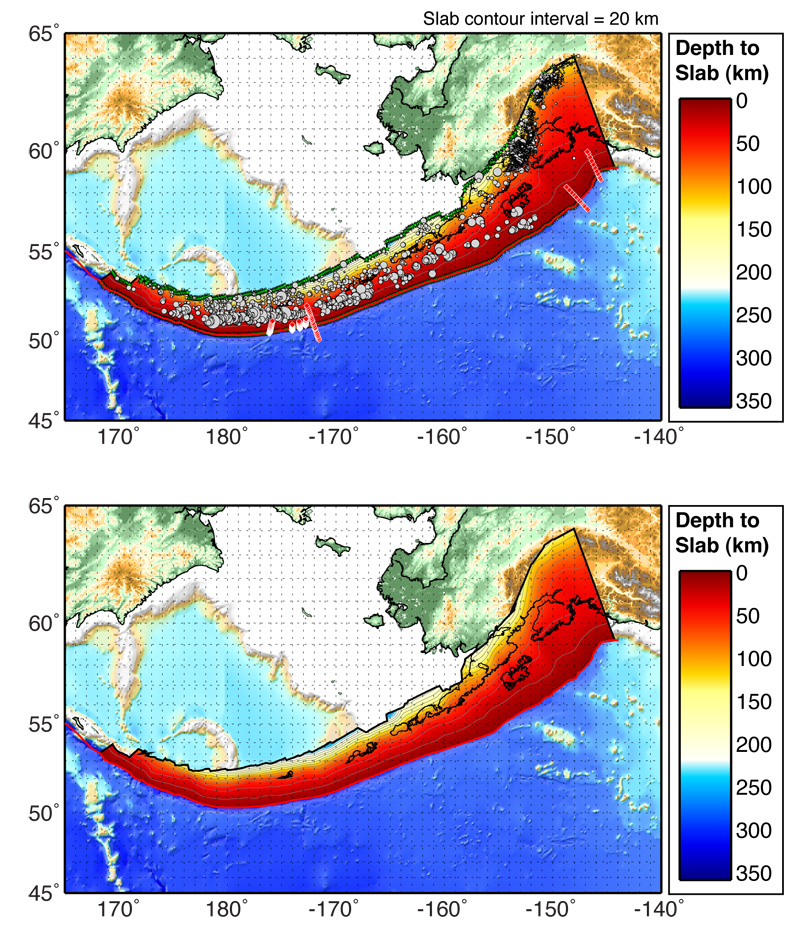
Fig 21.
"Slab
Models for Subduction Zones." USGS.
N.p., n.d. Web. 19 Apr. 2015.
<http://earthquake.usgs.gov/data/slab/>.
Images from the
1964 earthquake in Alaska...
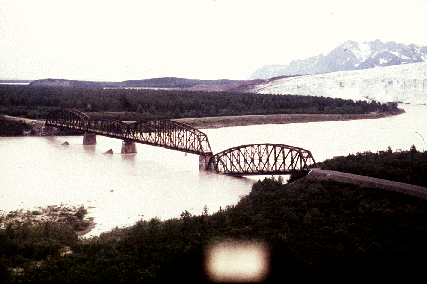
Fig 22. Failure of one span of the "Million Dollar" truss-bridge
over the Copper River.
Fig 23. A railway in Turnagain Arm that was severely displaced
by the earthquake.

Fig 24. Homes damaged by the landslide in Turnagain
Heights.
Fig 22-24. Reference
"Historic
Earthquakes." USGS.
N.p., n.d. Web. 19 Apr. 2015.
<http://earthquake.usgs.gov/earthquakes/states/events/1964_03_28.php>.