Engines
 Figure 1 http://outreach.phas.ubc.ca/phys420 /p420_08/Hiroko%20Nakahara /Pictures/heatEngine.jpg |
In an engine, heat (Q-in) is taken from a
heat source, then work is done, and heat (Q-out)
leaves the system. This is shown in Figure 1 to
the left. Figure 2 demonstrates this cycle on a
pressure vs volume graph. When heat is added to
the system, the pressure goes up. As work is
done by the gas, the pressure goes down while
the volume goes up. Then heat is taken out of
the system so the volume goes back down.
Finally, work is done on the gas so the pressure
rises and the volume fall. This process repeats
at a very fast pace. Monster Trucks are limited
to a 575 cubic inch engine. They use a methanol
injection system in order to get more torque.
These impressive engines can get around 1,250
foot-pounds of torque at over 4,000 rpm and more
than 1,500 horse power at 8,500 rpm. |
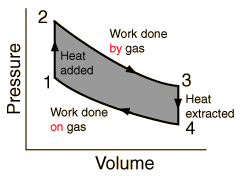 Figure 2 http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu /hbase/thermo/imgheat/heaengcyc.gif |

