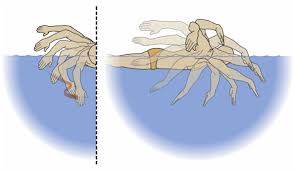
In order for a swimmer to reduce drag,
they must keep their body straight and symmetrical. This
is commonly known as streamlining. The swimmer keeps their
legs tightly together, their arms stretched in front of
them touching, and their biceps next to their ears. This
limits drag by limiting the frontal area of the swimmer in
the direction they are moving in.
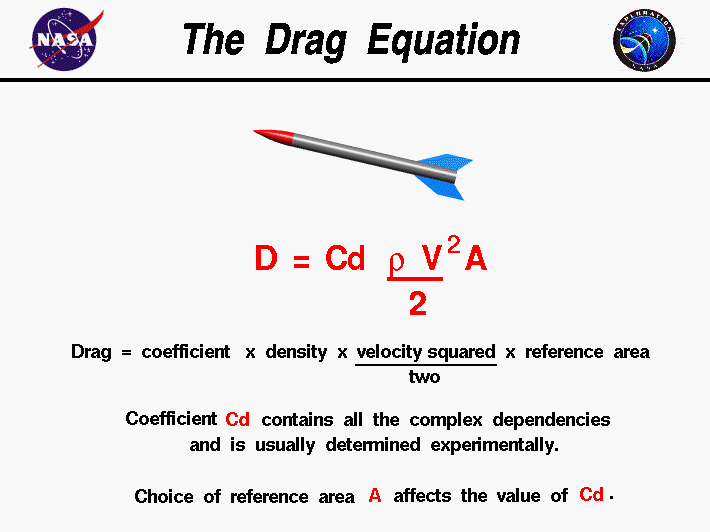
http://exploration.grc.nasa.gov/education/rocket/drageq.html

Buoyancy is needed to keep swimmers
afloat. In order to establish greater buoyancy, swimmers
try to press their chests down which causes the hips to
rise. This is called “pressing the T”. By “pressing the
T”, swimmers become parallel to the surface, which causes
them to float.
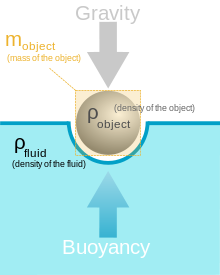
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/Buoyancy

http://www.womanaroundtown.com/sections/living-around/proper-breathing-more-efficient-workout
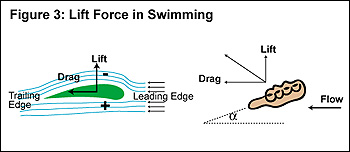
http://eng.jhu.edu/wse/magazine-summer-12/item/in-the-swim/