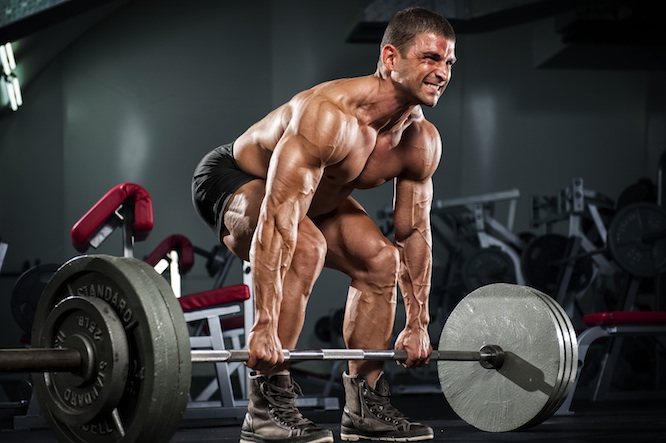
Much of weight lifting has to do with the simple concept of center of mass. In order to support any amount of weight, it must be in the position over the center of mass. For example, when squatting, it is best to focus your balance on the heel of your foot and the front of your foot. Do not lean too much on the toes or on the ball.
The lifting stance is dependent on the person. However, the wider the stance, the more side to side to side balance is provided. The more narrow the stance, the more fore-and-aft balance is provided. It is important to find a position which give equal balance for both ways. Generally shoulder width is good for many exercises. When the feet are further apart, there is a wider lateral area of balance. And if the feet are too narrow, there will be too little area to balance.
force=mass*acceleration
When you pick a weight up from its still position with zero acceleration, you are increasing its acceleration. When you pick a weight up slower, you are decreasing acceleration closer to zero.
With high intensity exercise, the speed of movement is important for success. For max effectiveness, the goal is to move the weight at the slowest velocity with smooth constant and steady speed. Also with less acceleration, there will also be less force, which essentially makes the lift safer.
It is important to lift weights, not throw them.