Antenna Characteristics
Frequency
Antennas operate by producing a standing wave in an unclosed electrical loop (a dangling wire). The frequency of the standing wave determines which classification of electromagnetic radiation is generated. The electromagnetic spectrum ranges from Radio at low energy levels to Gamma at high energy levels.
Frequency Bands
This continuous spectrum has been blocked off into bands for convenience.
Bandwidth
Bandwidth is simple the difference between the upper and lower limits an antenna can operate at. Cellphones for example operate between the 1850-1900 MHz range, a bandwidth of 50MHz.
Antenna Length
When an antenna is operating at its resonant frequency, it is able to maximize its efficiency and decrease wasted power. This resonance occurs when the antenna's circuit has a real resistance and zero reactance. For common antenna, the resonant frequency can be achieved with an antenna length of fractional wavelength. For a 300kHz radio wave, a antenna of only 250m is used (1/4 the 1km wavelength).
Gain
Measured in dB, the gain of an antenna is the ratio of its power delivered compared to the theoretical isotropic antenna. A gain of 3dB would equate to twice as much power delivered. Compared to other usages of decibel, here higher is better.
Radiation patterns
The radiation pattern of an antenna is a simple way to identify how signal strength (power) drops off with respect to distance.
Types of antennas
-
Isotropic
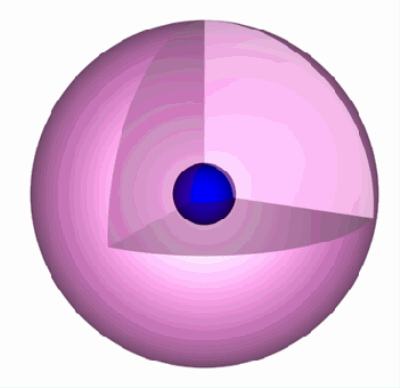
Cisco: Omni Antenna vs. Directional Antenna An isotropic antenna is one with a spherical radiation pattern. It has uniform signal strength at any location of fixed radius. This type on antenna is not actually possible and is only useful as an example or for comparison with other antenna.
-
Omni directional

antenna-theory.com: Radiation Pattern While the name might indicate a isotropic antenna, the omni refers to a single plane and not the whole 3d space. It produces a torus pattern with voids directly above and below the antenna. It is very common for cell-towers or wireless access points that need to cover large horizontal areas without the need for vertical coverage.
-
Directional

antenna-theory.com: Radiation Pattern More commonly recognised as dish antenna, this radiation pattern is designed for targeted long distance transmissions.
