 background image The Astronomer by Vermeer found at
http://fineartamerica.com/featured/vermeers-t
background image The Astronomer by Vermeer found at
http://fineartamerica.com/featured/vermeers-t background image The Astronomer by Vermeer found at
http://fineartamerica.com/featured/vermeers-t
background image The Astronomer by Vermeer found at
http://fineartamerica.com/featured/vermeers-t
Now we went through the how physics works, and how it affects
the setup. It's time to actually start to paint.
1) Drawing:
2) Mixing the Paint:
|
This simple depiction is the first step of the painting process, drawing. Often overlooked but still physics is involved by the friction between both the canvas and the pencil. The lead of the pencil leaves a residue do to it's lower friction coefficient than the canvas. If it was higher than the canvas the pencil would leave an indent. |
 Drawn by me Drawn by me |
|
Finally, step three is dragging the brush full of paint across the canvas. This process is best described using Newton's second law: F=mass*accelerationUsing this formula one has to take into account the force of friction discussed earlier.To make it more accurate one would have to find both the coefficient of kinetic friction, and calculate the friction of paint against each of the bristles. |
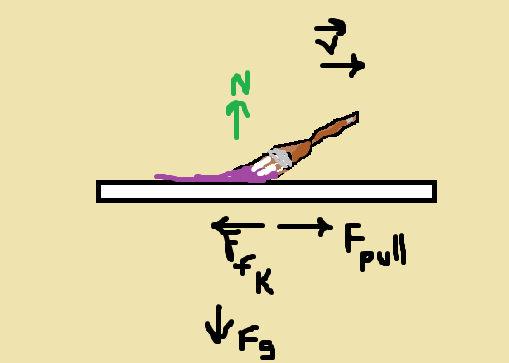 Drawn by me |
Mixing paint is the second step of the painting process. Now it is a little more complicated than the first step because it includes the difference in the paint densities. The density can be calculated by using the formula: |
 Drawn by me |