Systems and Processes (continued)
A thermodynamic process is the difference between the initial state and the final states within a thermodynamic system. Typically, each thermodynamic process is distinguished from other processes according to what parameters (as in temperature, pressure, or volume) are held fixed.
The six most common thermodynamic processes are described below:
An isothermal process occurs at a constant temperature.
An isobaric process occurs at constant pressure.
An isometric or isovolumetric process occurs at constant volume.
An adiabatic process occurs without loss or gain of heat.
An isentropic process occurs at constant entropy.
An isenthalpic process occurs at a constant enthalpy.
(Serway)
The first three processes are the most common process used to describe systems.
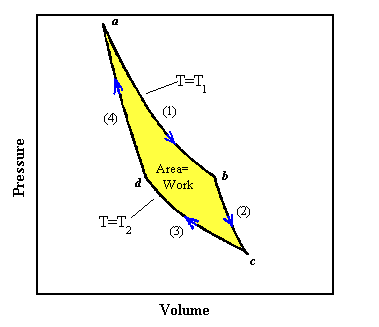
A more general diagram of a thermodynamic process is shown below.
http://electron9.phys.utk.edu/phys136d/modules/m3/images/carnot.gif