Home
The Field
Pitching Catching Bibliography
Physics of Hitting
The
most
basic concept of hitting is to put the bat on the ball.
Similarly, this basic concept
is also a
utilization one of the most basic theories of physics,  However, if one
wanted to learn
how to hit a home run
the individual would want
to use enough
force to hit the
ball over the fence for
a home run, and then at the same time to hit the ball
causing it to fly at an angle 45 degrees to the field, this would in
turn
result in the maximum distance to be achieved.
In order to
calculate the angle of trajectory of the ball after it is
hit, you can use the formula as outlined by the diagram to the right. The diagram shows all forces involved in
calculating the trajectory. This is done
by factoring in all forces (wind
resistance, loss of energy to sound,
velocities, etc.) and in doing so
ensuring that the net
energy and
momentum is conserved from the initial to the
final
However, if one
wanted to learn
how to hit a home run
the individual would want
to use enough
force to hit the
ball over the fence for
a home run, and then at the same time to hit the ball
causing it to fly at an angle 45 degrees to the field, this would in
turn
result in the maximum distance to be achieved.
In order to
calculate the angle of trajectory of the ball after it is
hit, you can use the formula as outlined by the diagram to the right. The diagram shows all forces involved in
calculating the trajectory. This is done
by factoring in all forces (wind
resistance, loss of energy to sound,
velocities, etc.) and in doing so
ensuring that the net
energy and
momentum is conserved from the initial to the
final 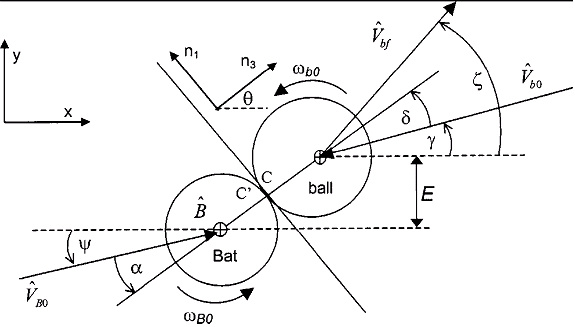 reaction.
The
hitting aspect
of
baseball through calculations and worldly physics allow
us to explain all reactions
between objects and
people that occur throughout the course of the game,
including the physics of pitching as well.
reaction.
The
hitting aspect
of
baseball through calculations and worldly physics allow
us to explain all reactions
between objects and
people that occur throughout the course of the game,
including the physics of pitching as well.

Symbol
Description
Value
G - Gravitational
acceleration constant 9.81 m/s2
m -
Static coefficient of friction - 0.5060.04 wood/
0.3560.03 aluminum
n -
Kinematic viscosity of air - 1.5e25 m2/s
CD - Drag coefficient
CL - Lift coefficient
Mb - Baseball mass - 0.145 kg ~5.1 oz!
MB 8 -
Bat
mass - 0.9 kg ~31.7 oz!
rb - Baseball radius - 0.0366 m ~1.44 in.!
rB - Bat barrel radius - 0.0350 m ~1.38 in.!
kB1 - Radius of gyration of bat for c.m. about n1
axis - 0.217 m ~8.54 in.!
kB2 - Radius of gyration of bat about n2
axis - 0.0231 m ~0.91 in.!
kb - Radius of gyration of ball about c.m. -
0.0247 m ~0.97
in.!
E - Undercut
distance
u -
Angle of common normal n3 from horizontal
a -
Bat swing angle from common normal
b -
Bat swing angle from horizontal
g -
Pitched ball velocity angle from horizontal
d - Pitched ball velocity angle from common normal Pic taken by K. Lauritzen (2005)
V ˆ
b0 - Pitched ball speed at plate
V ˆ
B0 - Pre-impact bat speed at B
ˆ
vb0 - Pre-impact
ball spin magnitude
vB0 -
Pre-impact bat spin magnitude
vb f - Post-impact
ball angular velocity
Vw - Wind velocity
V ˆ
b f -
Post-impact
ball c.m. velocity
Vb f - Post-impact
ball velocity at contact point
VBf -
Post-impact
bat velocity at contact point
z - Post-impact
ball velocity angle from
horizontal
1154 Am. J.
Phys., Vol.
71, No. 11, November 2003 Sawicki, Hubbard, and Stronge 1154