The Cavity Magnetron
The microwave oven
utilizes microwave radiation at 2.45 GHz to heat
food. A cavity magnetron is used in microwaves to
produce this radiation.
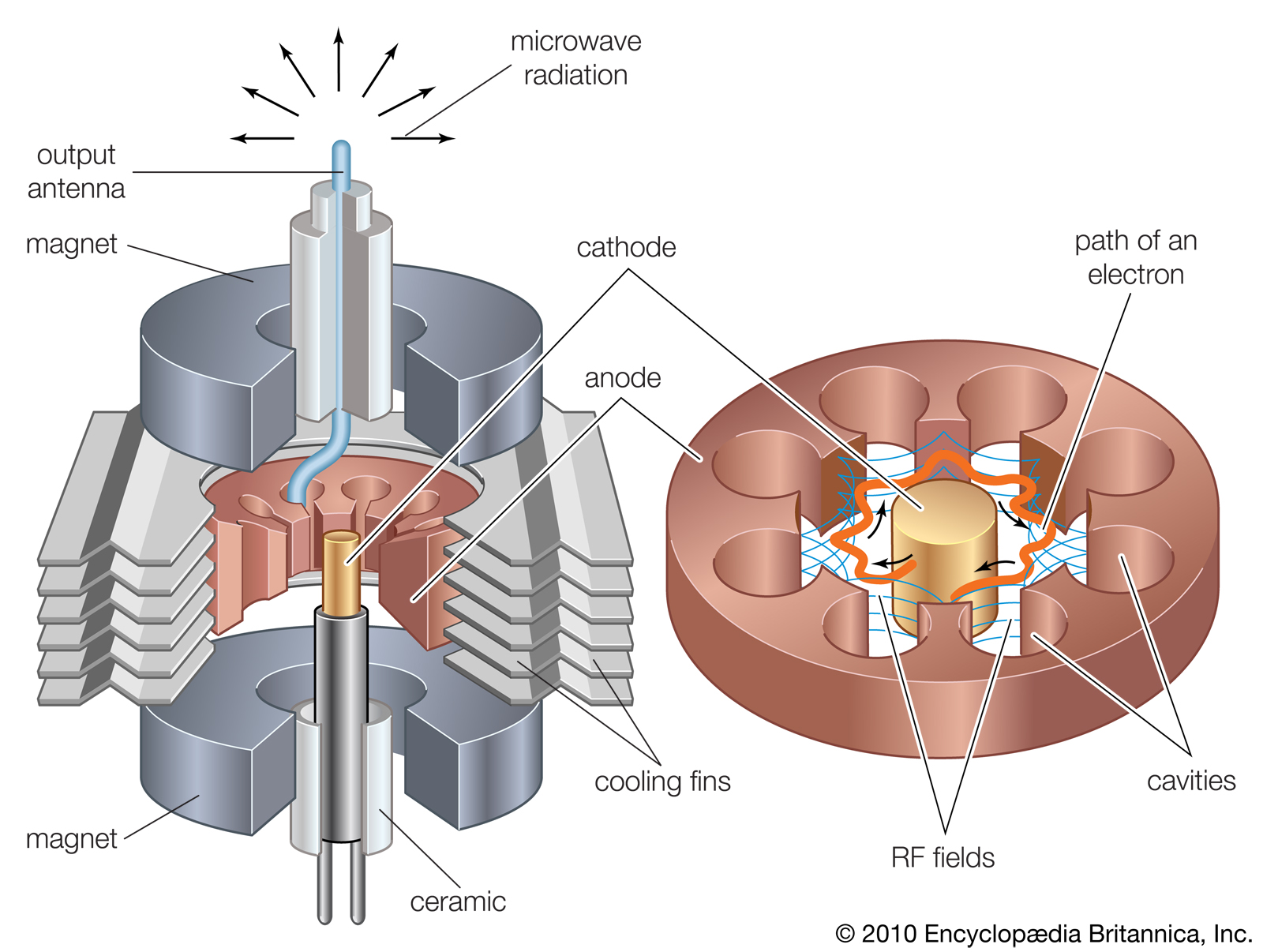
The cavity magnetron is a kind of vacuum tube. The vacuum tube consists of a sealed vacuum chamber with a tungsten filament running through the center.
When a large enough current is run through the filament electrons are shed and an electric field is created.
The permanent magnets on the top and bottom of the contain this field in the direction parallel to their propagation. The anode in the system is the copper ring surrounding the chamber. The relatively positive anode attracts the electrons.
This system of field containment causes the electrons to propagate outwards in a growing spiral, leading them through the series of cavities in the anode.
These cavities are designed such that an electromagnetic field passing through them will tend to resonate at a specific frequency- in this case 2.45 GHz.
These microwaves flow through the waveguide (a hollow structure with dimensions specific to the radiation that is being propagated. The walls of the waveguide reflect the electromagnetic waves, allowing them to be directed.) and into the cavity of the microwave.
The cavity magnetron is a kind of vacuum tube. The vacuum tube consists of a sealed vacuum chamber with a tungsten filament running through the center.
When a large enough current is run through the filament electrons are shed and an electric field is created.
The permanent magnets on the top and bottom of the contain this field in the direction parallel to their propagation. The anode in the system is the copper ring surrounding the chamber. The relatively positive anode attracts the electrons.
This system of field containment causes the electrons to propagate outwards in a growing spiral, leading them through the series of cavities in the anode.
These cavities are designed such that an electromagnetic field passing through them will tend to resonate at a specific frequency- in this case 2.45 GHz.
These microwaves flow through the waveguide (a hollow structure with dimensions specific to the radiation that is being propagated. The walls of the waveguide reflect the electromagnetic waves, allowing them to be directed.) and into the cavity of the microwave.