Electricity is a form of energy, described as the flow of
electrons between atoms. Atoms are described to be
arranged such that electrons are contained within shells around
the the nucleus. The nucleus lies at the center of these
shells, packed with protons and neutrons. The protons
exert a positive electrical charge while the electrons exert a
negative electrical charge, the resulting attractive electric
force is responsible for what holds together an atom. The
number of protons within the nucleus determines what element it
is, since the number of protons doesn't change. Within
each shell there are a certain number of energy slots. which can
be filled with an electron. When a shell of an atom is
filled, the electrons begin to fill the next shell. While
the electrons within the filled shells are more stable,
remainder electrons in the last shell are loosely attracted to
the atom and can be exchanged with other atoms. An atom is
charged when electrons are exchanged, referred to as ionization,
causing the atom to either become positively charged when
removed or negatively charged with the addition of
electrons.
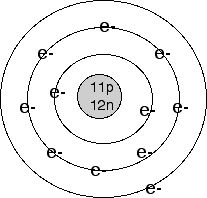 An Example of atomic shells (Na)
An Example of atomic shells (Na)