Geometry
In their most basic form and for the
sake of the simple physics I will apply to these vehicles,
motorcycles are composed of a frame, two wheels and tires, and
handlebars for steering. There are a lot more parts and factors that
make a motorcycle move but the physics involved can be described more
easily by simplifying the system in this way.
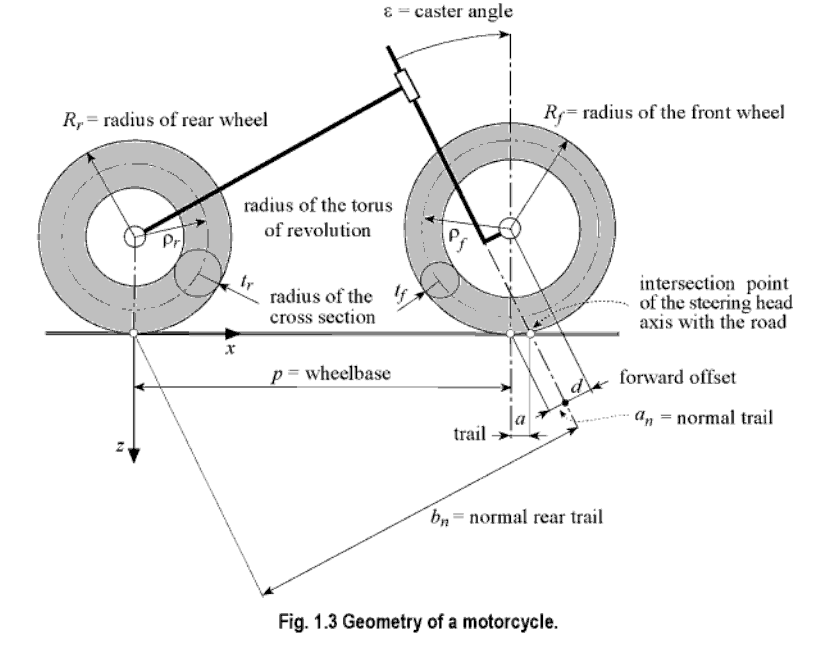
(Cossalter pg 4)
Geometry
This image makes it apparent that even with a simplified system
there
are still a lot of things having an effect on the success of the
vehicle. The wheelbase and trail are particularly important as
far as handling is concerned and are also two things that are commonly
changed when customizing motorcycles. A long wheel base will make
the ride smoother and more comfortable in a straight line but will also
diminish close handling capabilities. Alteration of the caster
angle, or the angle at which the forks sit, has an effect on the
handling of the motorcycle as well. An increase in the caster
angle, much like in wheelbase, creates better straight line stability
but decreases cornering capabilities (Cossalter).
Another important geometric feature that effects the handling of
the motorcycle is the trail. The trail is measured by the
intersection of the ground and the projection of where the forks (if
they were extended) hit the ground.
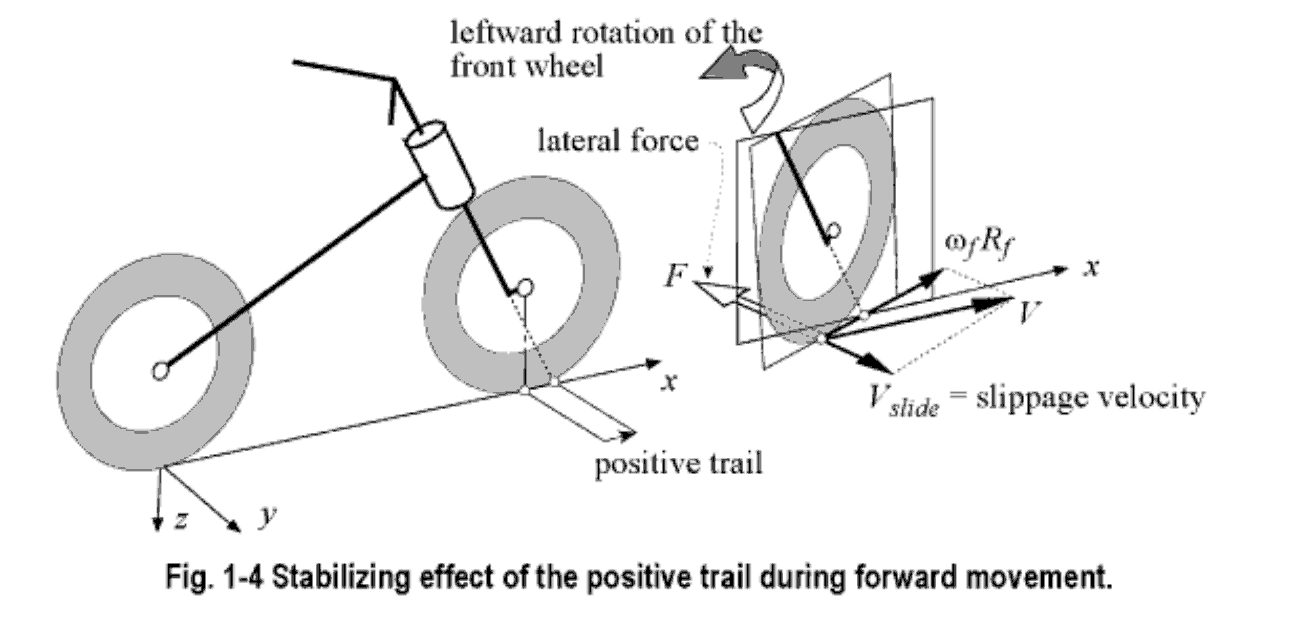
(Cossalter pg 6)