| |
 |
|
|
|
|
Kicking a ball is the main performance in soccer, and caused
by several scientific theories.
Velocity &
Acceleration
- Velocity (speed) and acceleration are related to the forces applied
on the ball. The speed of a person who runs towards the ball before a
kick affects acceleration, because the speed of the person running
before the kick will help to kick the ball harder with the higher
acceleration. In Newton's second law, force equals the mass times
acceleration F=ma. So the higher acceleration will apply more force to
the ball. (In the formula, higher 'a' will result a higher 'F').
Kinetic Energy & the
Conservation of Energy
- Kinetic
Energy is the energy acting on a moving object with the following
formula: ½mv² . By the conservation of energy, when an
object collides with another object, (assuming that no heat energy
produced) the total kinetic energy of the both objects has to be the
same after and before the collision. So for example, if a person kicks
a ball which is at rest on the ground, (ignoring all other conditions
except for velocity and mass) a part of the kinetic energy produced on
his foot by kicking will be transferred to the ball to maintain the
conservation of the energy.
Air Drag
- Air drag (sometimes called air 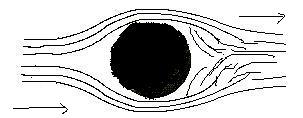 Air
drag
(sometimes
called
air
dragresistance)
is
the
friction
that
applies
in
the
air acting in an opposite direction to the relative motion of an
object. So the air drag is one of the reasons that the ball slows down
in the air after kicked. Drag Formula: FD = ½ ρu2ACD ( ρ:
density, u: velocity, A: area, CD: drag coefficient). This is why the
size, shape and density of the ball are very important factors for the
players. Air
drag
(sometimes
called
air
dragresistance)
is
the
friction
that
applies
in
the
air acting in an opposite direction to the relative motion of an
object. So the air drag is one of the reasons that the ball slows down
in the air after kicked. Drag Formula: FD = ½ ρu2ACD ( ρ:
density, u: velocity, A: area, CD: drag coefficient). This is why the
size, shape and density of the ball are very important factors for the
players.
Gravity
- Gravity is the force that pulls things down with 9.81 m/s2 Gravity
pulls the ball down while it travels in the air after kicked. That
causes the ball to fall to the ground, with the projectile motion along
with drag force.
Projectile motion 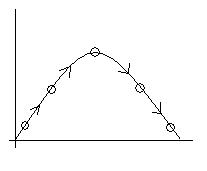
- Projectile
motion is a motion of an object in the air as the picture on the right,
caused by gravity and drag force (aka air resistance). When an object
is thrown in the air, it falls down to the ground because of the
gravity. And the velocity of the object and the drag force (air
resistance) changes the travel distance and time. The soccer ball
travels in a projectile motion through the air after being kicked. The
best example to see this motion would be a free kick and a corner kick.
Center of the Mass
- Center of
the mass is important in order to curve the ball when it is kicked.
Center of the mass is where the gravitational force is concentrated.
The formula for center of the mass is R = ( ∑m i
r i ) / M . Basically, if a person kicks
the exact center of a ball, the ball will not spin at all. However,
under normal circumstances, a person kicks the ball and it will spin
because we can't kick the exact center of the ball due to the unequal
surface of the shoes and the ball, and also due to the error of human
accuracy.
Bernoulli's Principal
-
Bernoulli's principal states that when speed of fluid or air flow
increases, its pressure or potential energy decreases. The following
formula explains the reason: Ρ + ½ρυ² + ρgh = constant ( Ρ:
pressure, ρ: density, υ: velocity). As you can see in the formula, if
the speed (velocity) increases, its pressure or potential energy has to
decrease to keep the constant value. This idea helps us to understand
the Magnus Effect (that will be explained in the following content).
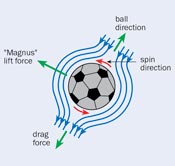 Magnus Effect Magnus Effect
- Magnus
effect states if an object travels while spinning through the air,
there is one side with faster speed and another with slower speed,
which will make the object curve. So the side of the ball, where the
direction of spin is same as the direction of air flow, has a faster
speed than the other side by the Magnus Effect. According to
Bernoulli's Principal, since the speed of the spin is faster, the air
pressure will be lower. This effect causes the ball to curve.
=====================================================================
Summary of Bibliography
http://www.slideshare.net/dodrums/the-physics-of-soccer
The
physics
of
soccer
http://www.bookrags.com/research/kinetic-energy-wop/
Kinetic Energy
http://www.serioussoccer.net/Documents/PhysicsofSoccer.pdf
The Physics of
Kicking a Soccer Ball
Science of
Soccer author by Wesson, John
=====================================================================
|
 |
|
|
|
 |
© 2010
Company Name
All Rights Reserved |
 |
|
|
 |
|