How does vitrification work?
 (Alcor)
(Alcor)
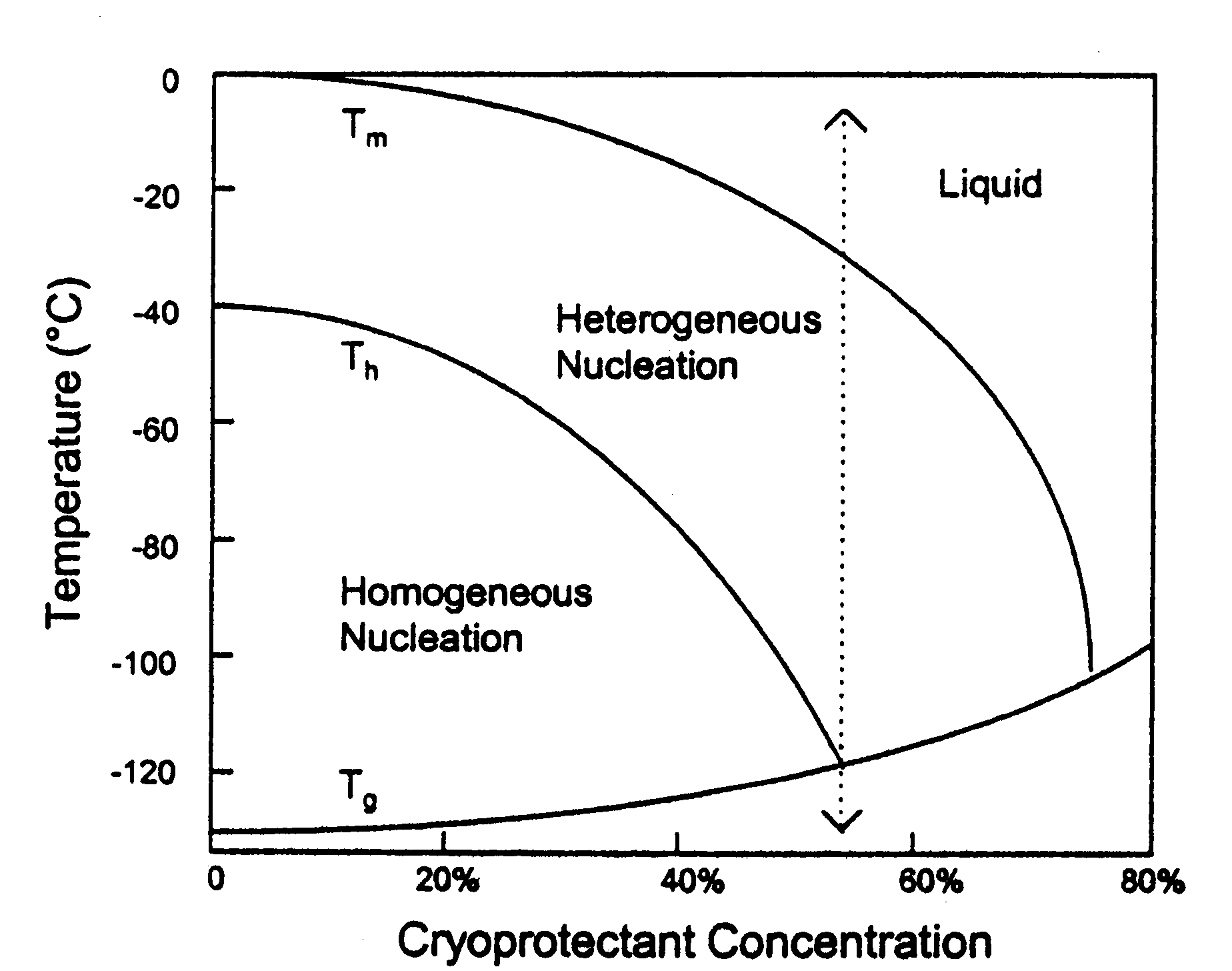
-"Adding high concentrations of chemicals called cryoprotectants to cells permits tissue to be cooled to very low temperatures with little or no ice formation. The state of no ice formation at temperatures below -120°C is called vitrification. It is now possible to physically vitrify organs as large as the human brain, achieving excellent structural preservation without freezing " (Alcor)

- Vitrification is able to avoid ice nucleation and growth, but this gets much more complicated in scientific terms.
-Vitrification uses such things as ice blockers and cryoprotectants to keep ice from forming.
"The other source of assistance for vitrification comes from ice blockers. While cryoprotectants slow ice-crystal growth and formation, ice blockers act specifically against the formation of the ice-nuclei which are necessary for freezing to begin " (Best).
Ice and water coexist when at freezing point, the amount of ice will not change as long as heat is not added or removed. The melting point of the crystal is a function of the radius of curvature for the crystal.
 (Best)
(Best)
For the derivation of the radius of curvature for the crystal see http://www.ucalgary.ca/~kmuldrew/cryo_course/cryo_chap6_2.html
With pure water we need a cluster with enough size to match the critical radius will be stable. It is hard to cool water to 30 degrees celsius (the temperature where the max cluster size is likely to occur spontaneously) without ice forming.
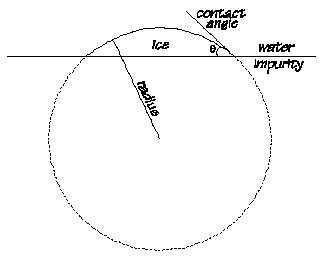
However, there are normally impurities in the water. "If the water molecules wet the surface of an impurity (that is large compared to water molecules) with a certain contact angle, then a portion of a sphere can form which has the critical radius which will therefore be stable. This type of nucleation is called heterogeneous nucleation" (Calgary).
 (Calgary)
(Calgary)
The contact angle theta is determined by the adhesive forces present and for a clean glass theta will equal zero degrees celsius. This means that the radius of the sphere is infinite meaning the nucleation temperature (when crystals would form in water) would be zero degrees celsius. (Calgary)
After all, the whole purpose of vitrification is to lower the temperatures at which molecules will stop in order to prevent freezing-damage.