Title Center of Gravity Torque & Friction Drag Circular motion Glossary References

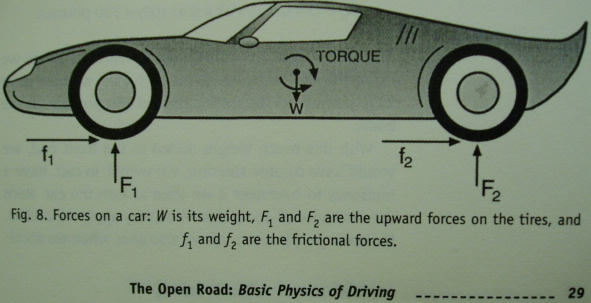
Frictional forces acting against the forward motion of the car slow the vehicle when it is braking at ground level, where inertia acts at the center of gravity to keeping it in motion and is higher off the ground. The same goes for acceleration only the inertia is zero initially so the forces acting upon the car to move it forward have to overcome these forces in the opposite direction of determined motion. These combative forces create a torque that try to roll the car, in whichever direction the fores are applied
Torque is the rotational force acting upon the center of mass of an object. If the car remains upright then the torques represented in the figure are equal and opposite keeping it from toppling. A well balance car is essential for the safety of the drivers and those around them because if the center of mass/gravity is not approximately halfway between the axels then the torques may not be equal and opposite because of the difference in perpendicular distance to the center of mass/gravity.