Chemistry of the Aurora
The name Aurora Borealis comes from the Greek goddess
of dawn, Aurora
and the Greek God of the northern wind, Boreas.
The color produced in an auroral display is the reaction of
charged particles from the sun reacting with atmospheric gases at differing
altitudes. These particles excite the valence electrons of the atmospheric gas
molecules, causing them to "jump" to a higher energy level. As the
electrons of the gas molecules settle back into their lower energy states, they
release photons, or the particles of light that are the aurora. Because energy
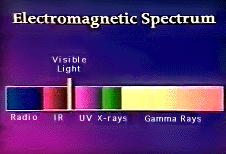
is light, the color of the light emitted in the aurora corresponds to a specific
wavelength of the electromagnetic spectrum.

Image taken from Nasa.gov: "The Electromagnetic Spectrum"
From the illustration above, it is understandable that the human eye cannot fully appreciate the colors of the aurora.