Sonar
Sonar (SOund Navigation And Ranging) is a method of detecting objects in water, used by all modern submarines. It is used because sound is able to travel much farther in water than light or radar. There are two types of sonar, active and passive.
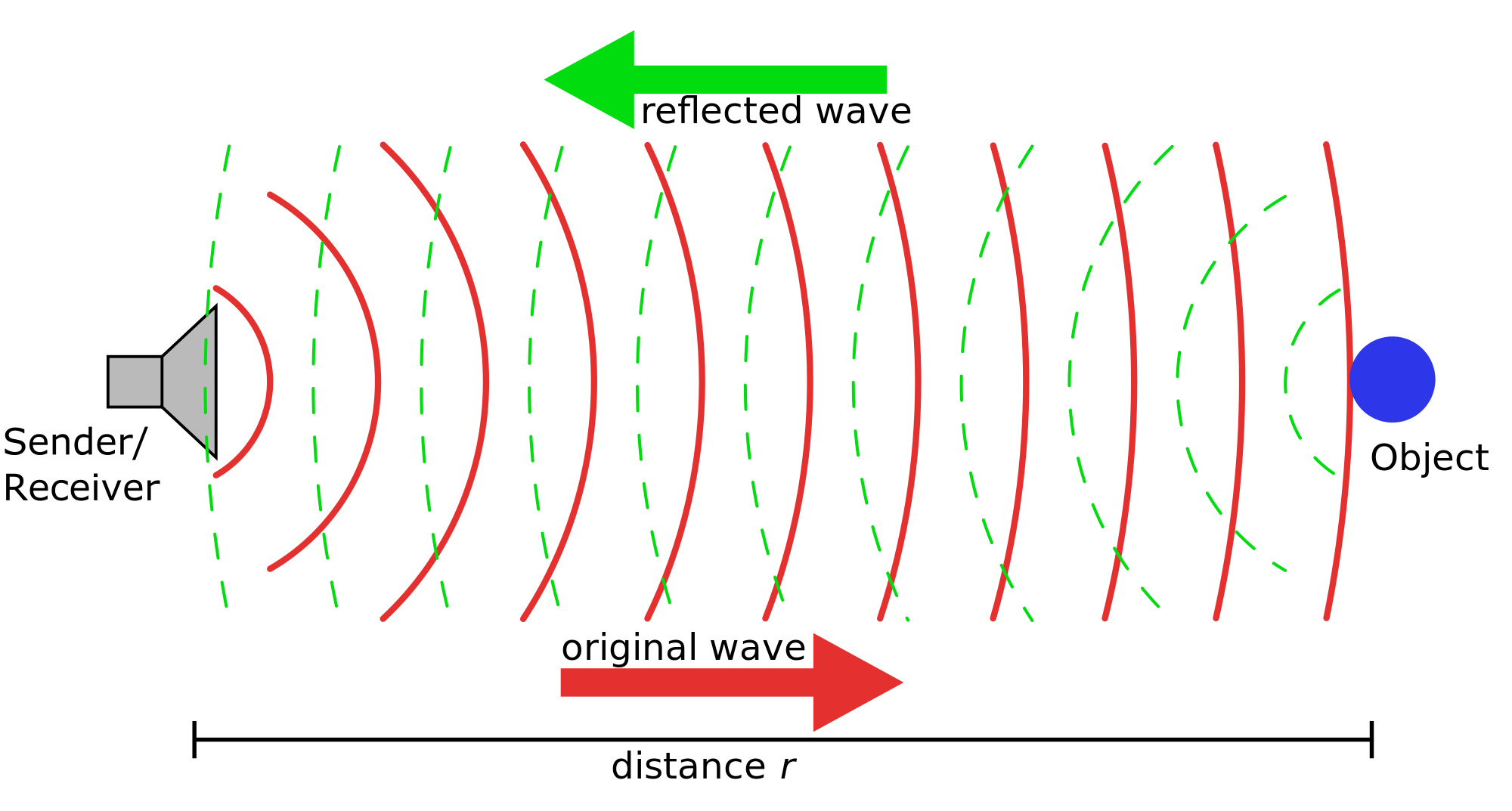
Active sonar involves releasing a wave of sound, called a ping, and measuring the time it takes to echo back to determine distances. The ping is normally in the range of 20 to 100 kHz.
Sonar ping sound.
Passive sonar differs from active sonar in that no sound is released by the sensor. It only picks up ambient sounds. Since passive sonar systems are very sensitive to sound, they cannot be used effectively on a loud vessel. Propellers and internal systems must be run quietly. It is used for both wildlife research, when active sonar pings could disturb animals, and the stealthy detection of enemy submarines, when a ping would give away one's own location.
Previous Next