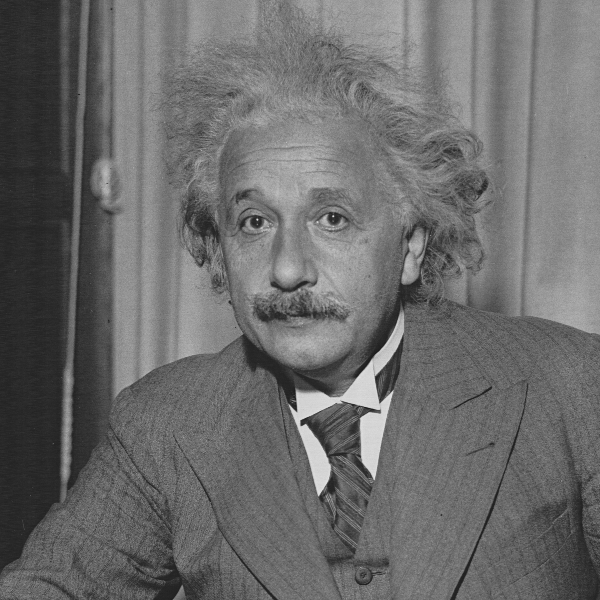
Relativism
 |
I'm not going to try to explain Einstein's theory of relativity. It is too complex and out of scope for this project. However there is an excellent tutorial with illustrations here that demonstrate the ideas that I will be talking about here. |
Albert Einstein. Found Here. |
Einstein's theory of relativity was the answer to Henry Poincare's statement in 1904, "Perhaps we must construct a new mechanics,... in which the speed of light would become an impassible limit." Ref. link. This can be shown with a very famous equation: E = mc2 Where E = energy, m = mass, c = speed of light and v = velocity. However this equation tells us the energy of a mass at rest only. We need an equation that tells us about moving objects. E = mc2 / sqrt(1 - v2/ c2) This less famous but complete equation describes the energy of massive objects at any speed. We know that energy and the speed of light are constants in a closed system. Thus if velocity is increasing then mass must be increasing as well. Any other explanation violates the conservation of energy or that the speed of light is a constant. Therefore as velocity gets close to c the mass of the object accelerating becomes infinitely large, and requires infinite force to keep accelerating it. Since there is no infinite force we cannot reach the speed of light. Of course to every rule there is an exception. Or is there? However it is important to point out that as technology gets better we will get closer to the speed of light. This means that a relativistic rocket is conceivable. |
Relativism |