Image taken from: http://www.unc.edu/~ncrani/friction1.htm
Friction is also a major contributing factor in the ball's distance, and movement along the field.
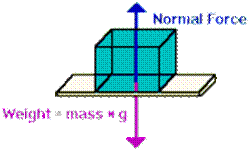
ffriction = μ N
The
frictional force is equal to the normal force multiplied
by the coeffecient of friction.
The
more friction between the ball and the field, the slower the speed
of the ball. Less friction will allow the ball to travel smoother and
faster. The coefficient of friction will tell us "how fast or slow a
ball will travel". The higher the coefficient, the more friction,
therefore the slower the ball is capable of traveling without another
force acting on it continuously.
Frictional
forces are always tangential to the surfaces they interact with.