Internet Guide to Electronics
Voltage, Current, and Resistance
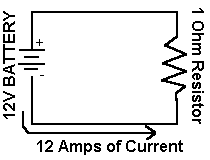
When working with circuits, the three basic elements to anaylizing the circuit are voltage, current, and resistance. These three readings help you find out all the information you need on how the cicuit will work and they are all related to eachother through Ohm's law which states that Voltage is equal to current times resistance. Now, you might be wondering why this is importent to people, can't you just throw in some components into a circuit and call it good? No, don't we all wish it worked like that. If you look at the circuit above it is made up of two components, a battery and a resistor. Now, if you didn't know how much resistance that resistor had but new the voltage that the battery put out and the current that was in the circuit, well, you could solve the resistance. The basic understanding of the three elements is that voltage pushes the current and the resistances slows it down. If you think of it in terms of plumbing, the voltage is the pressure on water in a pipe, the current is the flow and speed of the water in the pipe, and resistance is the junk in the pipe that slows the water down cause you haven't used a pipe cleaner. Now for the nitty gritty on the three elements.
Voltage
Voltage is read in terms of volts (V) which has a relationship of 1 volt is equal to 1 Joule per Coulomb. Voltage is the work required per unit charge to move those charges. Voltage is the workhorse of all circuits and almost ALL basics circuits contain a voltage source such as the battery in the above diagram. Here is a picture to help understand the idea of how voltage works. It is going back to the plumbing aspect seeing as how the two can be so closely related.

Internet Guide to Electronics
As you can see, the voltage is like a piston which pushes the "fluid" through a pipe. This is representing the voltage pushing current through the circuit. Voltage can appear in other situations besides circuits, such as voltage that is in an electric field. Voltage in those situations don't directly relate to the circuitry at hand so they will be skipped.
Current
Current is the rate of flow of electrons through a circuit. So when you have a battery connected to a wire pushing those electric charges, it creates a current. Current can be thought of as the amount of charge that passes through a space per unit time (a second usually). Current is read in the unit of ampere (A). 1 Ampere is equal to 1 Coulomb per second.
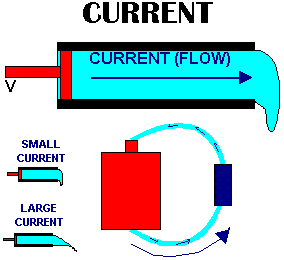
Internet Guide to Electronics
As you can see from the picture above, the current flow moves around the completed loop of the circuit. If the voltage was kept at a constant number then the current would be higher with the less amount of resistance, showing that it can flow more easily.
Resistance
This is where the voltage and current meet up at, the resistance. Resistance is the opposition to the flow of electrons. It is the jagged rocks in the river that slow down the movement of the water, it is the clog in your drain that slows down the speed of the flow. VIVA LA RESISTANCE! The Resistances of an object can be calculated if you know its length, cross-sectional area and its conductivity. Resistance in an object (a wire for example) is the length of the object over the conductivity times the cross-sectional area. Now, most things that are used for resistance aren't listed with their conductivity too much, instead they go by resistivity which is 1 over conductivity. This makes the resistance of an object to come out to be the resitivity times the length, all over the cross-sectional area. Resistivity is given in Ohms per meter and an example resistivity would be 1.7 x 10^-8 (which is copper, the most commonly used wire material). Because most circuits use short pieces of wire, their resistance is often not included when equating out the values of a circuit. When you are comparing two resistances and the wire is to the exponenet of -8, it tends not to matter. Most resistance that is looked at in a circuit is from actual resistors. These are used to reduce the current in a circuit or in some cases, increase the voltage.
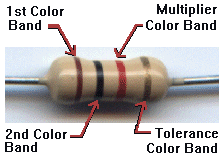
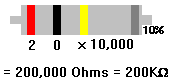
Internet Guide to Electronics
The picture above is of an actual "resistor" which is a component of a circuit. The bands across a resistor are a color code scheme to label how much resistance the resistor has. Here is a link to a site that let you play with the resitance of a resistor.
How they all relate
How the three elements relate has been stated by the fast and simple V=IR. Well, here is some visual aids to help you SEE what the relationship is trying to say.
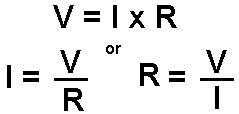
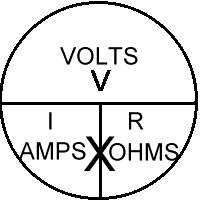
Internet Guide to Electronics
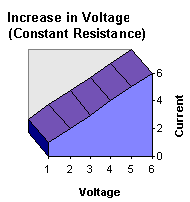
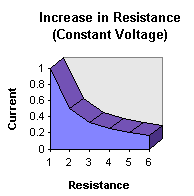
Internet Guide to Electronics
Here is a cool link to help you do the math of equating the different values of either voltage, current, or resistance.
Go back to the main page HERE.
Move on to Capacitors, Inductors, and Diodes.