Atmospheric Effects
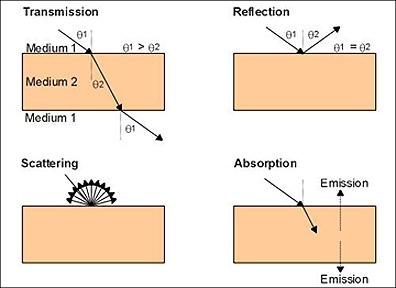
- Gases such as carbon dioxide, water vapor, oxygen, ozone interfere with electromagnetic energy absorption and reflection. The figure below illustrates the effects of interaction behaviors with different matter.
- The illustrations below depict the four types of interaction between electromagnetic radiation and matter.
- Atmospheric scattering (illustrated at bottom left of figure above) of light results in haze and reduced image sharpness.
- There are 3 types of atmospheric scattering that depend on the wavelength of the electromagnetic radiation (EMR) and the size of the atmospheric particle the radiation is interacting with.
- Rayleigh scattering: the diameter of particles << wavelength of EMR
- preferentially scatters EMR at the wavelength of blue light...this is what makes Earth skies appear blue
- Mie scatter: diameter of particles = wavelength of EMR
- caused primarily by water vapor, fumes, smoke, and dust
- results in red/orange appearance of evening Earth skies or when forest fires or volcanoes are putting particulates and smoke into the atmosphere
- Non-selective scatter: diameter of particles >> wavelength of EMR
- all wavelengths of light scatter equally
- caused by dust, clouds, and fog