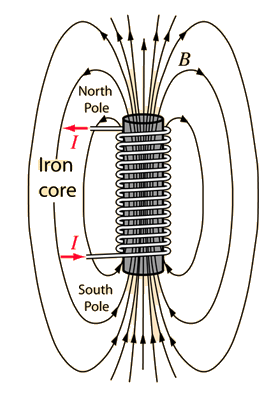

Electromagnets have
iron cores wrapped with
wire.
Emf induced in rod traveling through magnetic field by Michael
Faraday
Electrical Generator
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/magnetic/elemag.html http://www.s-cool.co.uk/a-level/physics/lenzs-law/revise-it/lenzs- https://www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/boundless-physics-textbook
http://hyperphysics.phy-astr.gsu.edu/hbase/magnetic/elemag.html http://www.s-cool.co.uk/a-level/physics/lenzs-law/revise-it/lenzs- https://www.boundless.com/physics/textbooks/boundless-physics-textbook
| How do Magnets
work? The underlying aspects of magnetism consist of the
science of magnetic fields. Magnets have magnetic fields
that push and pull objects toward and way from them.
When an electron moves it generates a magnetic field
with two poles north, and south respectively. Science
cannot explain why this happens yet, it's just a factor
of the universe that exists. However, we do know that
opposites attract. The north pole attracts the south
pole, and two of the same poles will resist each other.
|
Electro-Motive Forces
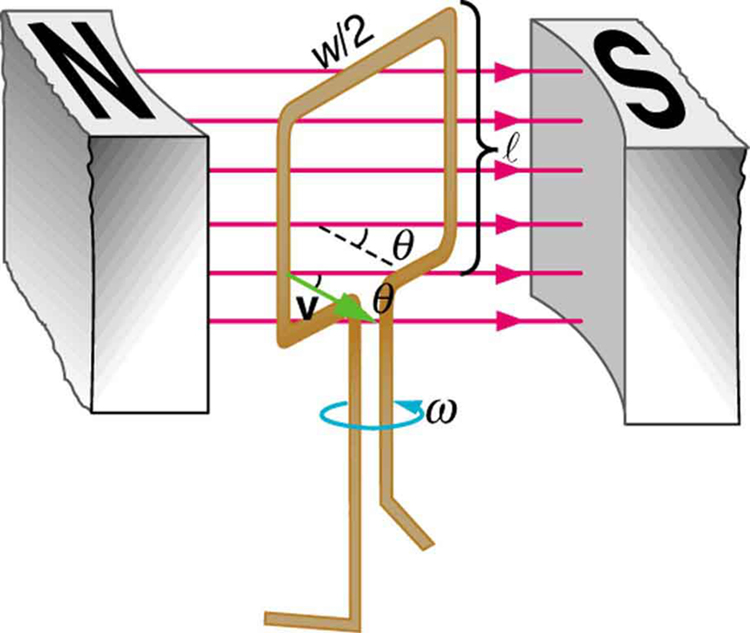
Electrical Generator
Rod Traveling Through a Magnetic Field
| (EMF)—The voltage generated by a battery
or by the magnetic force according to Faraday's Law. It
is measured in units of volts, not newtons, and thus, is
not actually a force. |
Electrical Generator
| Electric generators are devices that
convert mechanical energy to electrical energy. They
induce an electromotive force (EMF) by rotating a coil
in a magnetic field. It is a device that converts
mechanical energy to electrical energy. A generator
forces electric charge (usually carried by electrons) to
flow through an external electrical circuit. |
Rod Traveling Through a Magnetic Field
| The rod will move across the field
and cause an electrical current and a change in flux as
well. This change in flux over time can be measured and
modeled by the EMF equation. The direction of motion of
the rod is acting perpendicular to the direction of the
flux. If the flux changes, an emf will be induced. There are therefore three ways an emf can be induced in a loop:
We can apply Faraday's law and the right hand rule to
find out which direction the emf, flux and magnetic
field are going. |