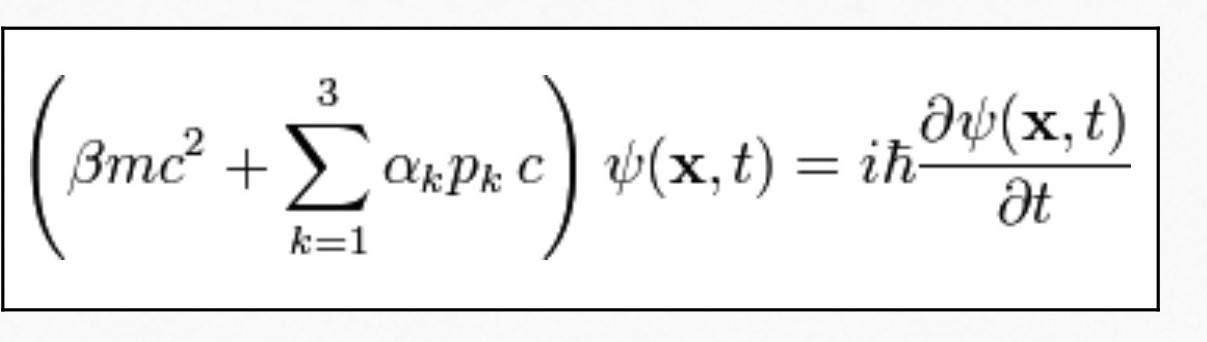Born August 8, 1902 in Bristol, United Kingdom, Dirac
first studied electrical engineering and received his
B.S. in 1921. However, he went on to obtain for his
Ph.D. in mathematics, and eventually became Lucasian
Professor of Mathematics at Cambridge in 1932.
Dirac's work mainly focused on theoretical physics and
mathematics. His most important contribution to physics
was his renown wave equation. With his work he helped
bridge both quantum and relativity theories. In 1933 he
shared the Nobel Prize in Physics with Erwin Schrodinger
for the discovery of new forms of atomic theory.